Google Workspace Source

The Google Workspace Source collects a list of users from the Google Workspace Users API. It securely stores the required authentication, scheduling, and state tracking information.
Data sources
The Google Workspace integration consumes data from the Google Workspace Users API. The Google Workspace Source retrieves data once per 24 hours based on user input for either deleted users or all users in a domain.
Metadata Field
Metadata fields will be set, if the integration is configured with the SIEM forward option. See Metadata Fields table below:
| Fields | Value |
|---|---|
_siemVendor | |
_siemProduct | Workspace |
_siemDataType | Inventory |
States
A Google Workspace Source tracks errors, reports its health, and start-up progress. You’re informed, in real-time, if the Source is having trouble connecting, if there's an error requiring user action, or if it is healthy and collecting by utilizing Health Events.
A Google Workspace Source goes through the following states when created:
- Pending. Once the Source is submitted, it is validated, stored, and placed in a Pending state.
- Started. A collection task is created on the Hosted Collector.
- Initialized. The task configuration is complete in Sumo Logic.
- Authenticated. The Source successfully authenticated with Google.
- Collecting. The Source is actively collecting data from Google.
If the Source has any issues during any one of these states, it is placed in an Error state.
When you delete the Source, it is placed in a Stopping state. When it has successfully stopped, it is deleted from your Hosted Collector. On the Collection page, the Health and Status for Sources is displayed. Use Health Events to investigate issues with collection. Hover your mouse over the status icon to view a tooltip with a count of the detected errors and warnings. You can click on the status icon to open a Health Events panel with details on each detected issue.
Set up and Configurations
In this configuration, you will set up a Google Workspace source account and configure it to be authorized and authenticated to use Google Workspace. To set up a Google Workspace account, you need to configure Google service account credentials. You may refer to the Google Documentation for more information.
Creating Service Account
To create service account credentials, follow the steps below:
- Navigate to the Google Console service account page.
- Log in with your credentials.
- Create a new project or select from the existing projects.
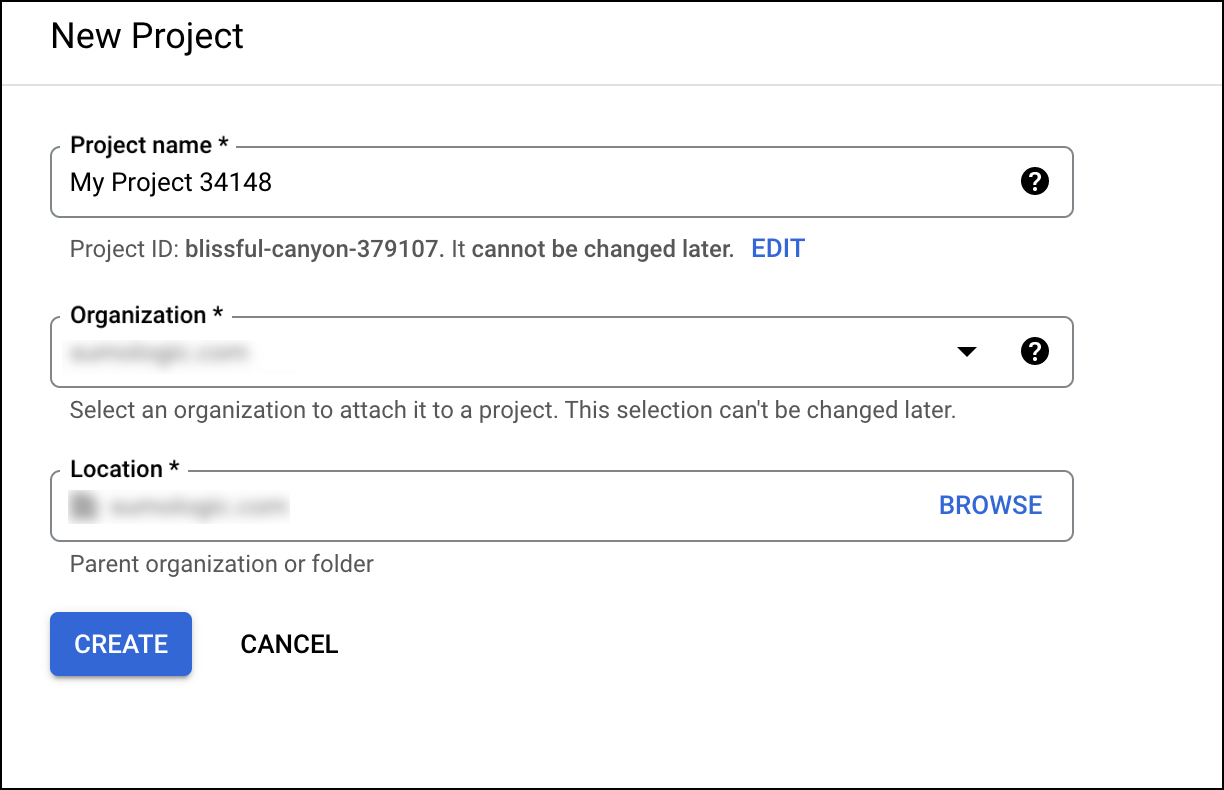
- Enable Admin SDK API to have an administrator access. To locate this setting, you can search for Admin SDK in the search bar. Then select the Enable button.
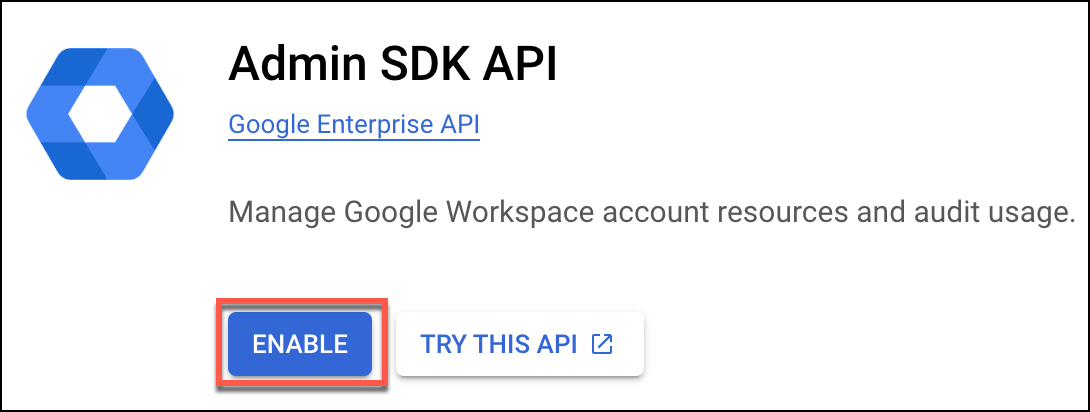
- You will be redirected to the Admin dashboard page. Select the Credentials option from the left navigation.
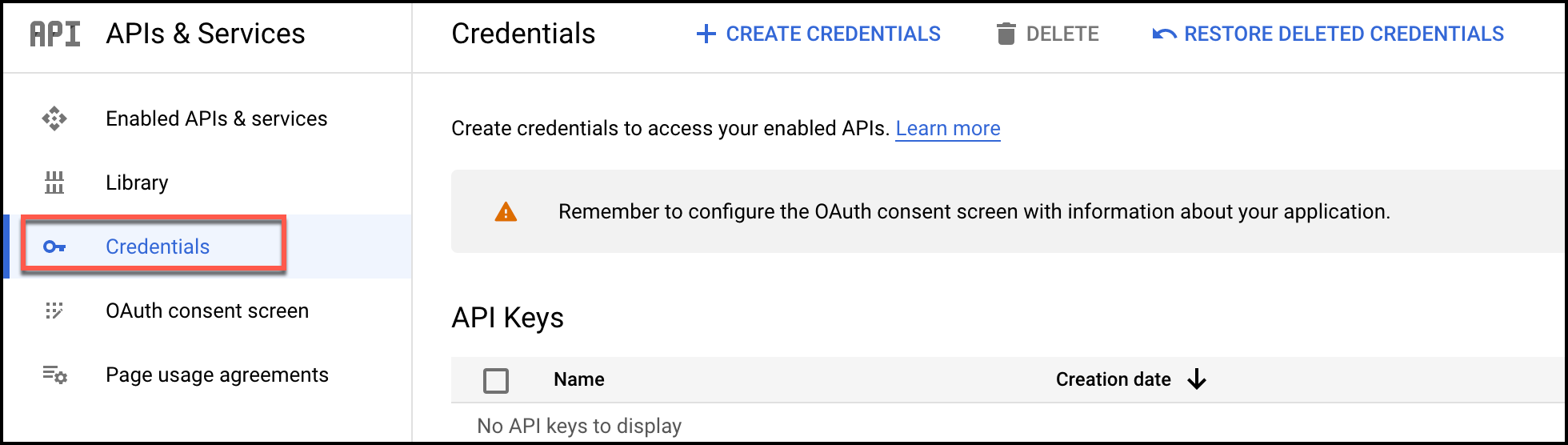
- Click the
 button at the menu bar of the Google Console page, and select Service account from the options that appear.
button at the menu bar of the Google Console page, and select Service account from the options that appear.
- After entering the service account details, you may leave the Optional fields and continue to click Done.
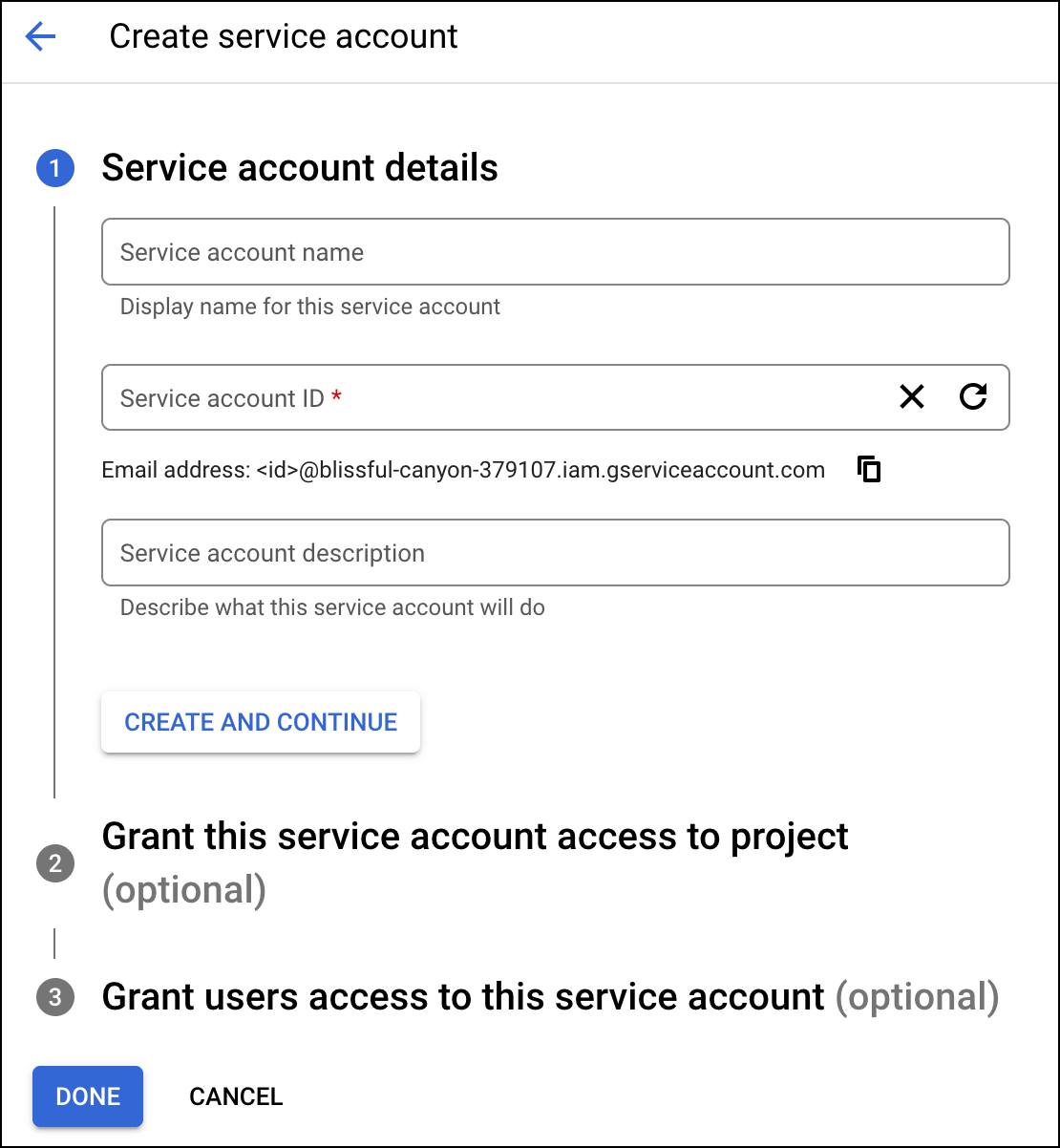
- To create JSON for the service account, you must create a key. Select the service account email to navigate to the Keys tab.
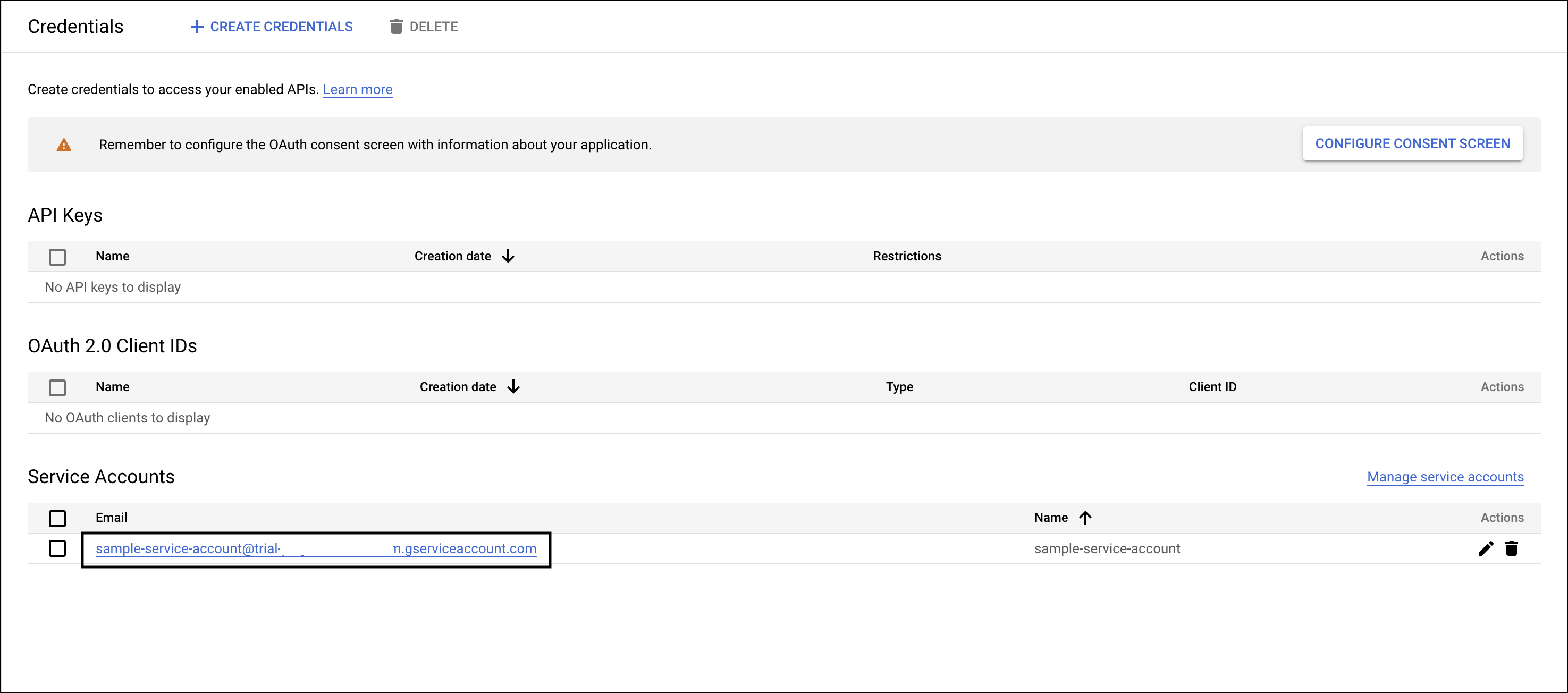 .
. - Click Keys tab on the same service account page.
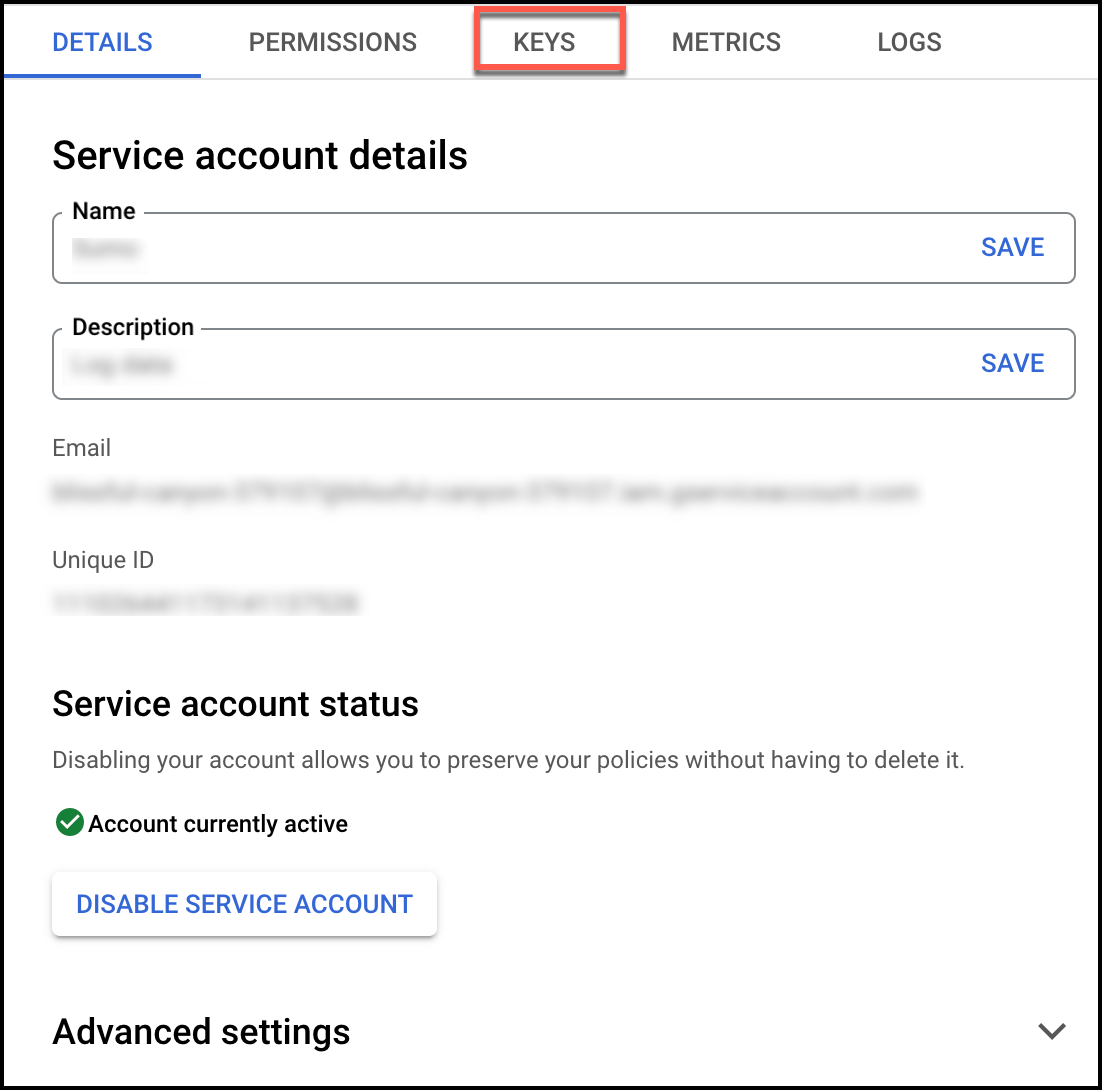
- From Add Key dropdown, select Create new key. At the prompt, select JSON and click Create to create a key
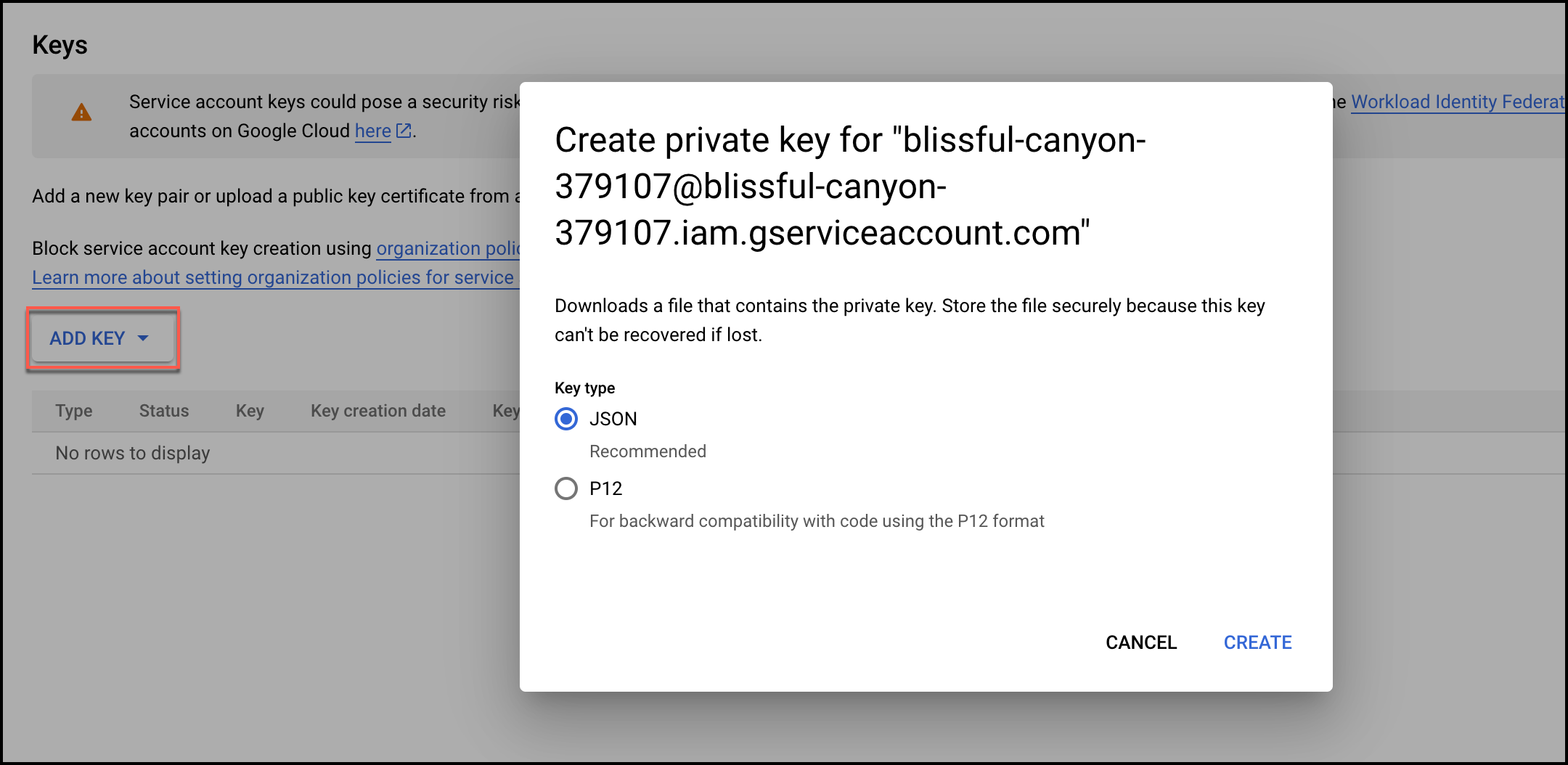
- JSON for the service account is automatically downloaded. To see what the JSON looks like, and how the JSON fields map to the fields you'll configure, see the JSON Example below.
Domain-wide Delegation
To add domain-wide delegation to your service account using the client ID or Key generated in above section, follow the steps below:
- Navigate to the Google Console service account page.
- Select your service account.
- Go to Advanced settings section.
- Under Domain-wide delegation, find your service account's Client ID. Click
to copy the client ID value to your clipboard.
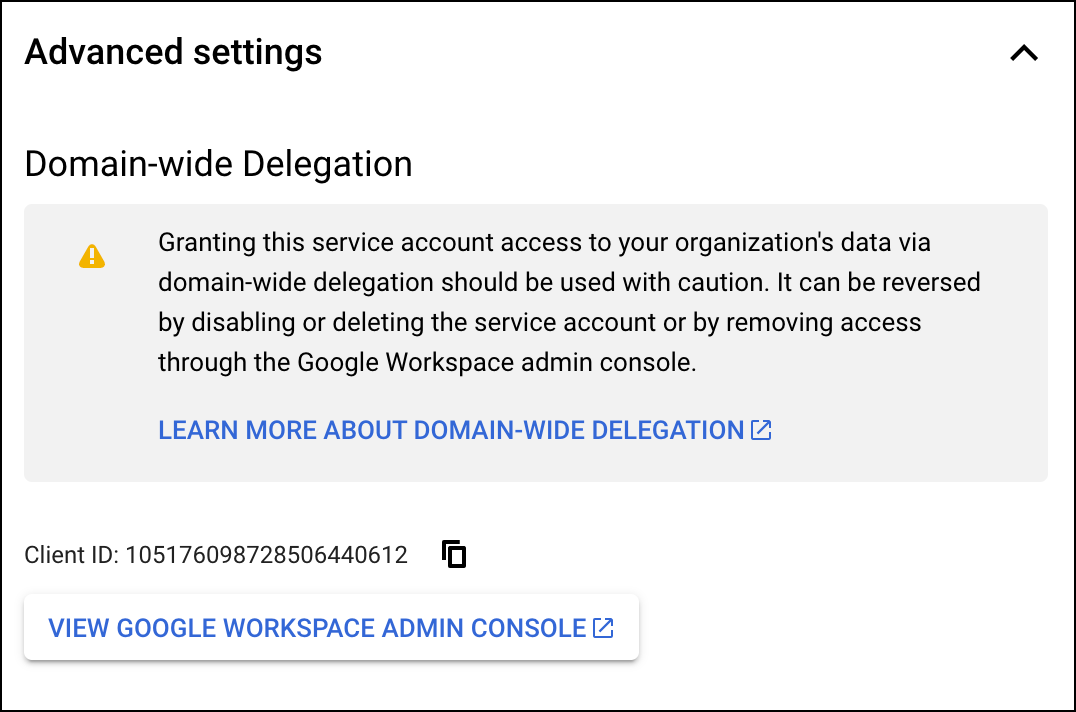
- If you have super administrator access to the relevant Google Workspace account, click View Google Workspace Admin Console, then sign in using a super administrator user account and continue following the steps in the section below.note
If you don't have super administrator access to the relevant Google Workspace account, contact a super administrator for that account and send them your service account's Client ID and list of OAuth Scopes so they can complete the following steps in the Admin console.
Adding OAuth Scope
OAuth Scope enables delegated access to a user's resources on a service, such as Google, without exposing the user's credentials to the third-party application. By adding the necessary OAuth scopes, you are specifying the level of access the service account has to your resources, while also ensuring security and privacy.
From the Google admin console, go to Security section, then click API Controls.
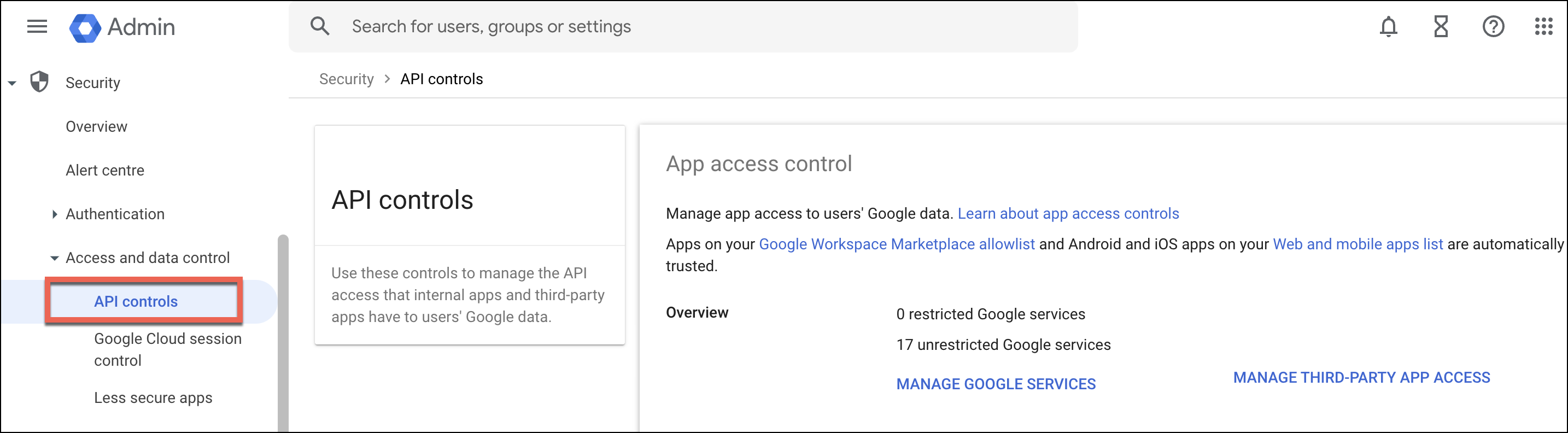
To add the OAuth scopes, locate the settings under Manage Domain Wide Delegation section.

Click Add new.
In the Client ID field, paste the client ID you copied in step 5 of the Creating Service Account section.
In the OAuth Scopes field, enter a comma-delimited list of the scopes required by your application.
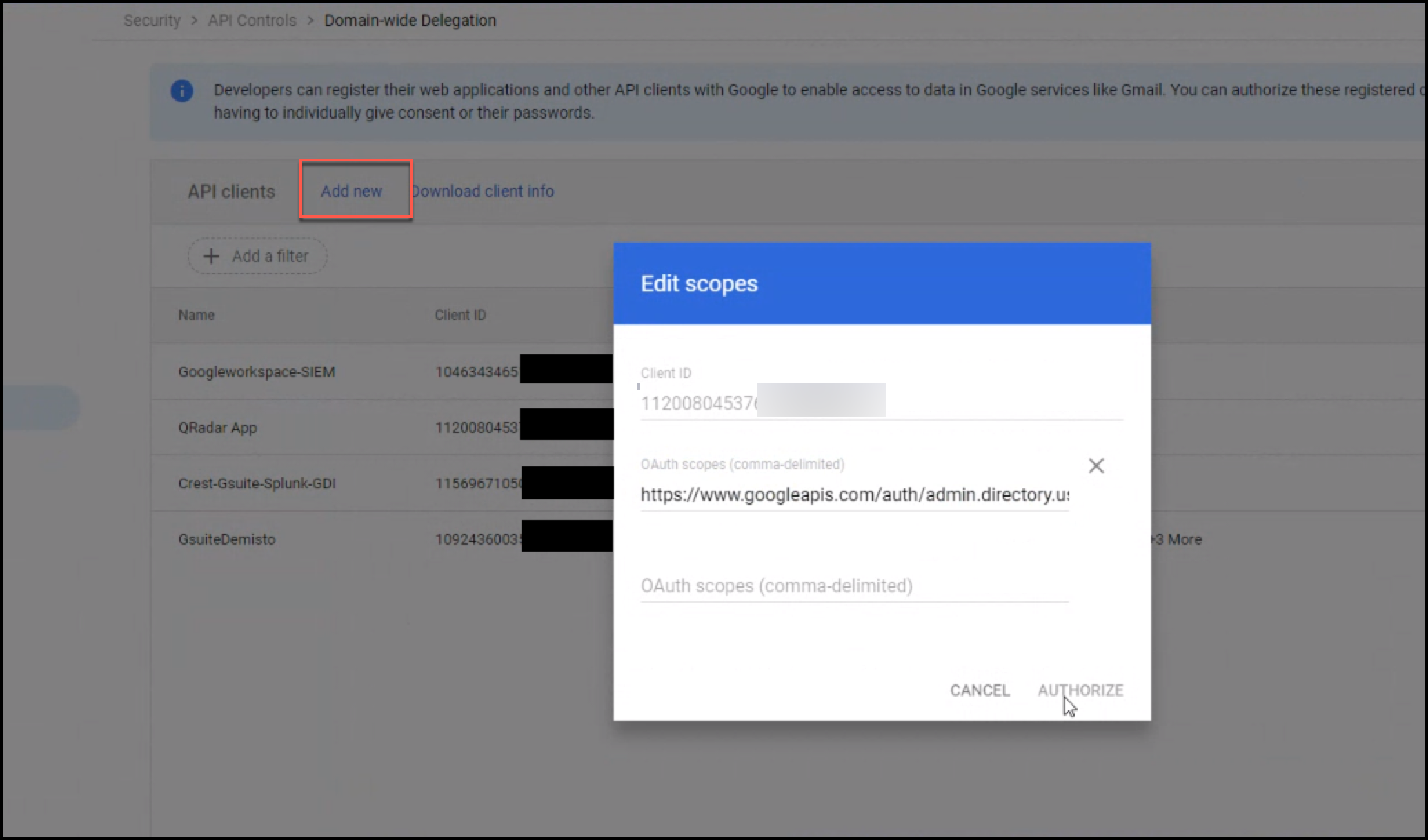 .
.You can add any of the following OAuth scopes. Note the ones you select, you'll need to provide them when configuring the Sumo Logic Google Workspace Source.
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user.readonly
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platformnoteTo ensure that you are authorized to fetch the users' details, it is recommended to add an OAuth scope to your Google Workspace service account. Adding the appropriate OAuth scope(s) maintains security and privacy for your users.
Learn more about OAuth scopes:
Create a Google Workspace Source
When you create a Google Workspace Source, you add it to a Hosted Collector. Before creating the Source, identify the Hosted Collector you want to use or create a new Hosted Collector. For instructions, see Configure a Hosted Collector.
To configure a Google Workspace Source:
- In Sumo Logic, select Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
- On the Collectors page, click Add Source next to a Hosted Collector.
- Select Google Workspace.

- Enter a Name to display for the Source in the Sumo web application. The description is optional.
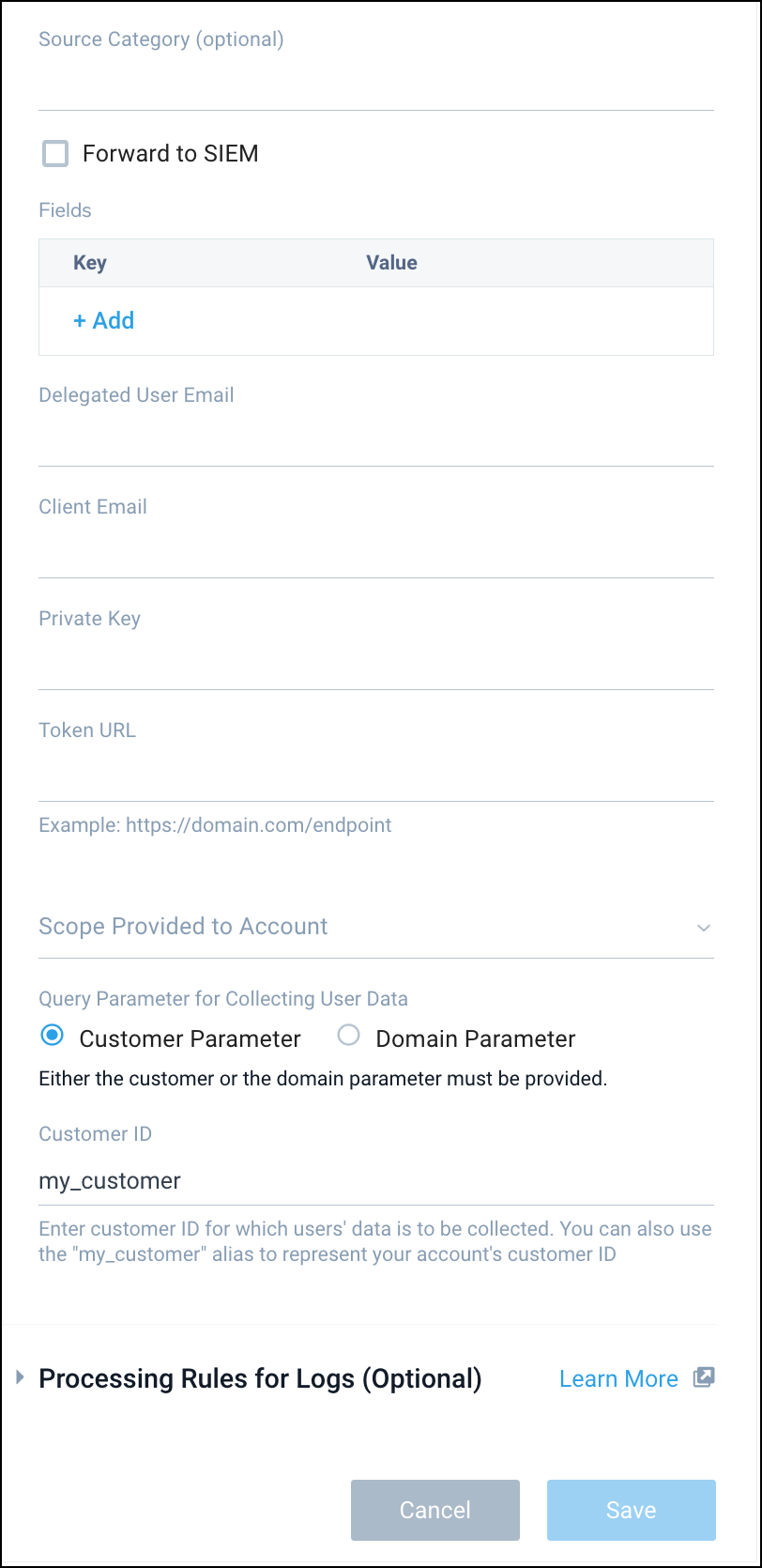
- (Optional) For Source Category, enter any string to tag the output collected from the Source. Category metadata is stored in a searchable field called
_sourceCategory. - Forward to SIEM. Check the checkbox to forward your data to Cloud SIEM Enterprise and become part of User Inventory. When configured with the Forward to SIEM option the following metadata fields are set:
_siemVendor: Google_siemProduct: Workspace_siemDataType: Inventory
- (Optional) Fields. Click the +Add Field link to define the fields you want to associate, each field needs a name (key) and value.
A green circle with a check mark is shown when the field exists in the Fields table schema.
An orange triangle with an exclamation point is shown when the field doesn't exist in the Fields table schema. In this case, an option to automatically add the nonexistent fields to the Fields table schema is provided. If a field is sent to Sumo that does not exist in the Fields schema it is ignored, known as dropped.
- The Delegated User Email is the email address of the user you want to call the API on behalf of. This user should have the necessary permissions to view the details of other users in your Google Workspace domain, such as an Admin role. At a minimum, the user should have the
Users:Read permission. Learn more about Domain-Wide Delegation of Authority: - Provide the Client Email, Private Key, and Token URL you got in the JSON file after you created service account credentials in the Creating Service Account above.
- Provide the same Scope you defined for your service account during the Adding OAuth Scope above.
- The Query Parameter for Collecting User Data section provides two options, Customer or Domain Parameter. See the Directory API documentation from Google for details.
- Customer ID. The unique ID for the customer's Google Workspace account. In the case of a multi-domain account, to fetch all groups for a customer, fill this field instead of domain. You can also use the
my_customeralias to represent your account'scustomerId. ThecustomerIdis also returned as part of the Users resource. - Domain: The domain name. Use this field to get fields from only one domain. To return all domains for a customer account, use the
customerquery parameter instead.
- When you are finished configuring the Source, click Submit.
Error types
When Sumo Logic detects an issue it is tracked by Health Events. The following table shows the three possible error types, the reason the error would occur, if the Source attempts to retry, and the name of the event log in the Health Event Index.
| Type | Reason | Retries | Retry Behavior | Health Event Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ThirdPartyConfig | Normally due to an invalid configuration. You'll need to review your Source configuration and make an update. | No retries are attempted until the Source is updated. | Not applicable | ThirdPartyConfigError |
| ThirdPartyGeneric | Normally due to an error communicating with the third party service APIs. | Yes | The Source will retry for up to 90 minutes, after which it quits. | ThirdPartyGenericError |
| FirstPartyGeneric | Normally due to an error communicating with the internal Sumo Logic APIs. | Yes | The Source will retry for up to 90 minutes, after which it quits. | FirstPartyGenericError |
Restarting your Source
If your Source encounters ThirdPartyConfig errors, you can restart it from either the Sumo Logic UI or Sumo Logic API.
UI
To restart your source in the Sumo Logic platform, follow the steps below:
- Open the Collection page, and go to Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
- Select the source and click the information icon on the right side of the row.
- The API usage information popup is displayed. Click the Restart Source button on the bottom left.
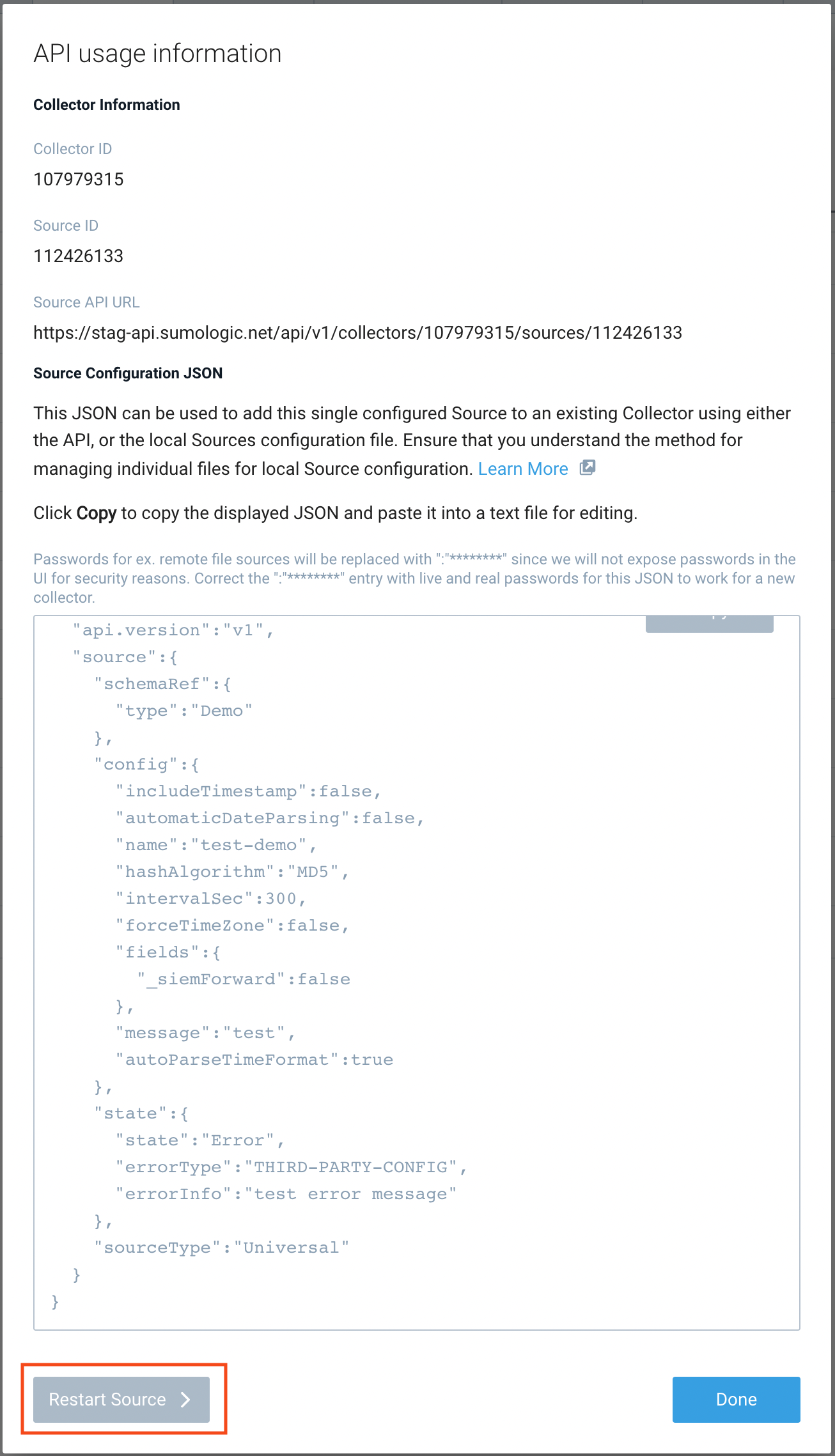
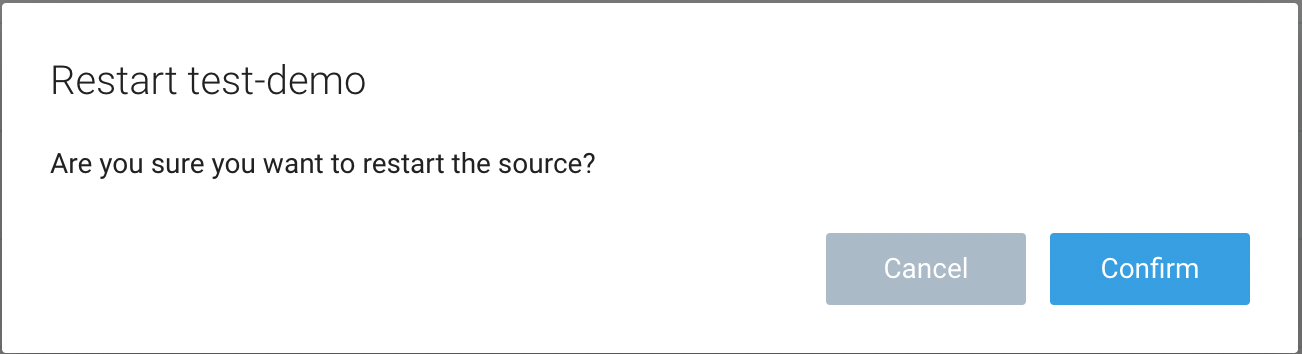
- Click Confirm to send the restart request.
- The bottom left of the platform will provide a notification informing you the request was successful.

API
To restart your source using the Sumo Management API, follow the instructions below:
- Method:
POST - Example endpoint:
https://api.sumologic.com/api/v1/collectors/{collector_id}/sources/{source_id}/action/restart
Sumo Logic endpoints like api.sumologic.com are different in deployments outside us1. For example, an API endpoint in Europe would begin api.eu.sumologic.com. A service endpoint in us2 (Western U.S.) would begin service.us2.sumologic.com. For more information, see Sumo Logic Endpoints.
JSON configuration
Sources can be configured using UTF-8 encoded JSON files with the Collector Management API. See how to use JSON to configure Sources for details.
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| config | JSON Object | Yes | Contains the configuration parameters for the Source. | |
| schemaRef | JSON Object | Yes | Set to {"type":"Google Workspace"}. | not modifiable |
| sourceType | String | Yes | Set to Universal. | not modifiable |
The following table shows the config parameters for a Google Workspace Source.
| Parameter | Type | Required? | Default | Description | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
name | String | Yes | Type a desired name of the Source. The name must be unique per Collector. This value is assigned to the metadata field _source. | modifiable | |
description | String | No | null | Type a description of the Source. | modifiable |
category | String | No | null | Type a category of the source. This value is assigned to the metadata field _sourceCategory. See best practices for details. | modifiable |
fields | JSON Object | No | JSON map of key-value fields (metadata) to apply to the Collector or Source. Use the boolean field _siemForward to enable forwarding to SIEM. | modifiable | |
clientEmail | String | Yes | Provide the Client Email you got in the JSON file after you created service account credentials | modifiable | |
delegatedUserEmail | String | Yes | Provide the super-administrator email address for the domain that granted access to the service account you created. | modifiable | |
privateKey | String | Yes | Provide the Private Key you got in the JSON file after you created service account credentials | modifiable | |
tokenURL | String | Yes | Provide the Token URL you got in the JSON file after you created service account credentials | modifiable | |
scope | String | Yes | Provide the same Scope you defined for your service account | modifiable | |
queryParam | Boolean | No | true | By default, the Customer parameter is selected with a CustomerID value of my_customer. To assign a different CustomerID provide the customerID parameter. Set to false to use the Domain parameter. You need to provide the domain parameter when false. | modifiable |
| customerID | String | No | my_customer | The unique ID for the customer's Google Workspace account. modifiable | |
domain | String | No | (except when queryParam is set to false.) | The domain name. Use this field to get fields from only one domain. modifiable |
JSON Example
{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "sample_project",
"private_key_id": "asdfgh1234556",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\nsample_private_key\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "sample_project@sample_service_account.com",
"client_id": "12345678",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/sample_url.com"
}
Mapping of fields from the above JSON to the input form.
| Fields of above JSON Example | Input Fields |
|---|---|
| client_email | Client Email |
| private_key | Private Key |
| token_uri | Token URL |