Azure Event Hubs Source
If you're using our new Cloud-to-Cloud source collection, see Migrating from Azure function-based collection to Event Hub Cloud-to-Cloud Source.
The Azure Event Hubs Source provides a secure endpoint to receive data from Azure Event Hubs. It securely stores the required authentication, scheduling, and state tracking information.
Collecting data from Azure Event Hubs using this Cloud-to-Cloud collection source has a supported throughput limit of 1MB/S (86GB/day) for a named Event Hub egress rate. We recommend using the Azure Functions model if you require higher throughput.
The Azure platform can be configured to export logs to one or more Event Hub destinations. Platform logs include:
Third party apps or services can be configured to send event data to Event Hubs as well, including Auth0.
This Source is available in the Fed deployment.
Prerequisites
Create an Event Hub using the Azure portal by navigating to Event Hubs in the Azure Portal.
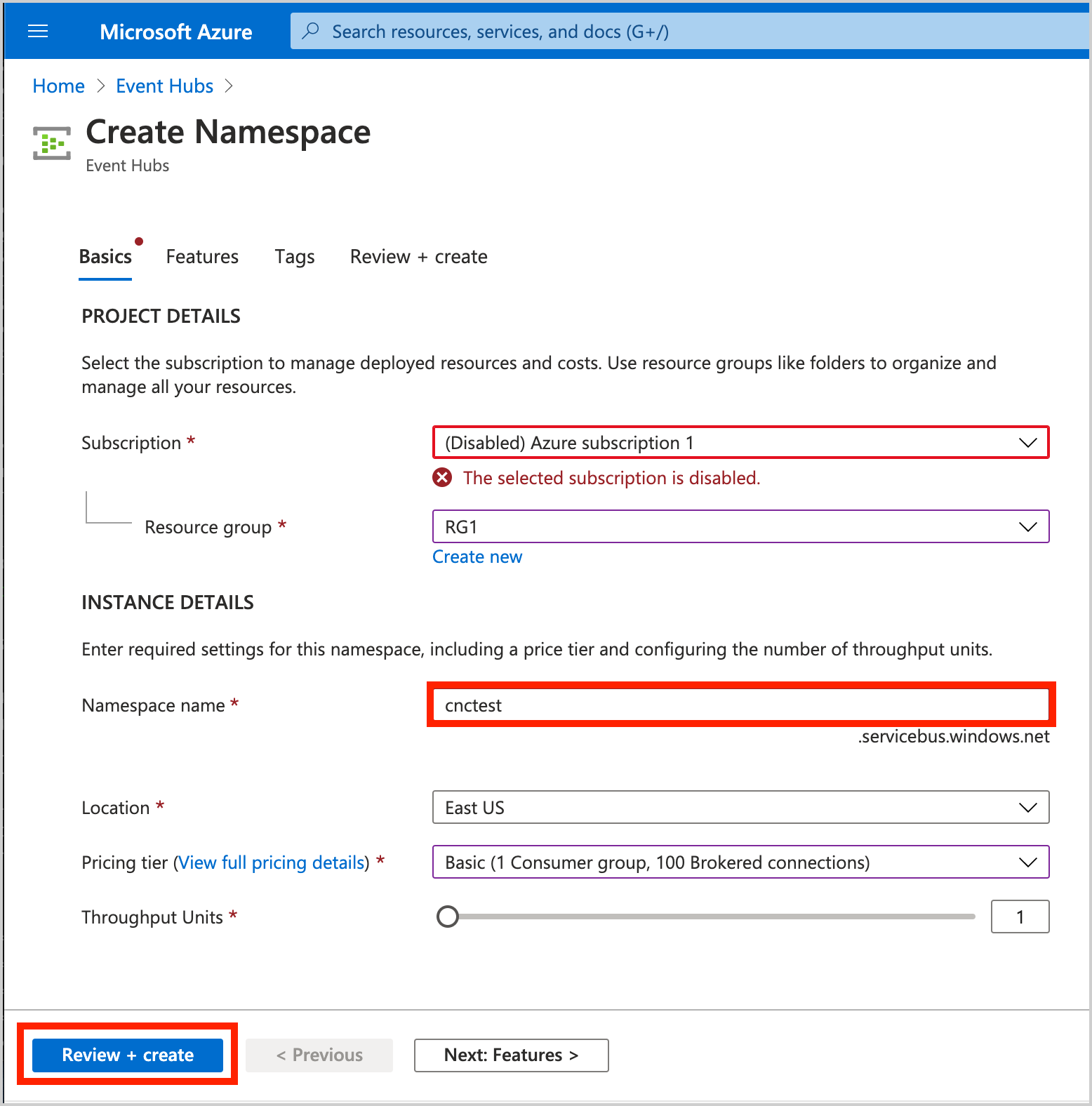
Create an Event Hubs namespace. In this example, Namespace is set to cnctest:

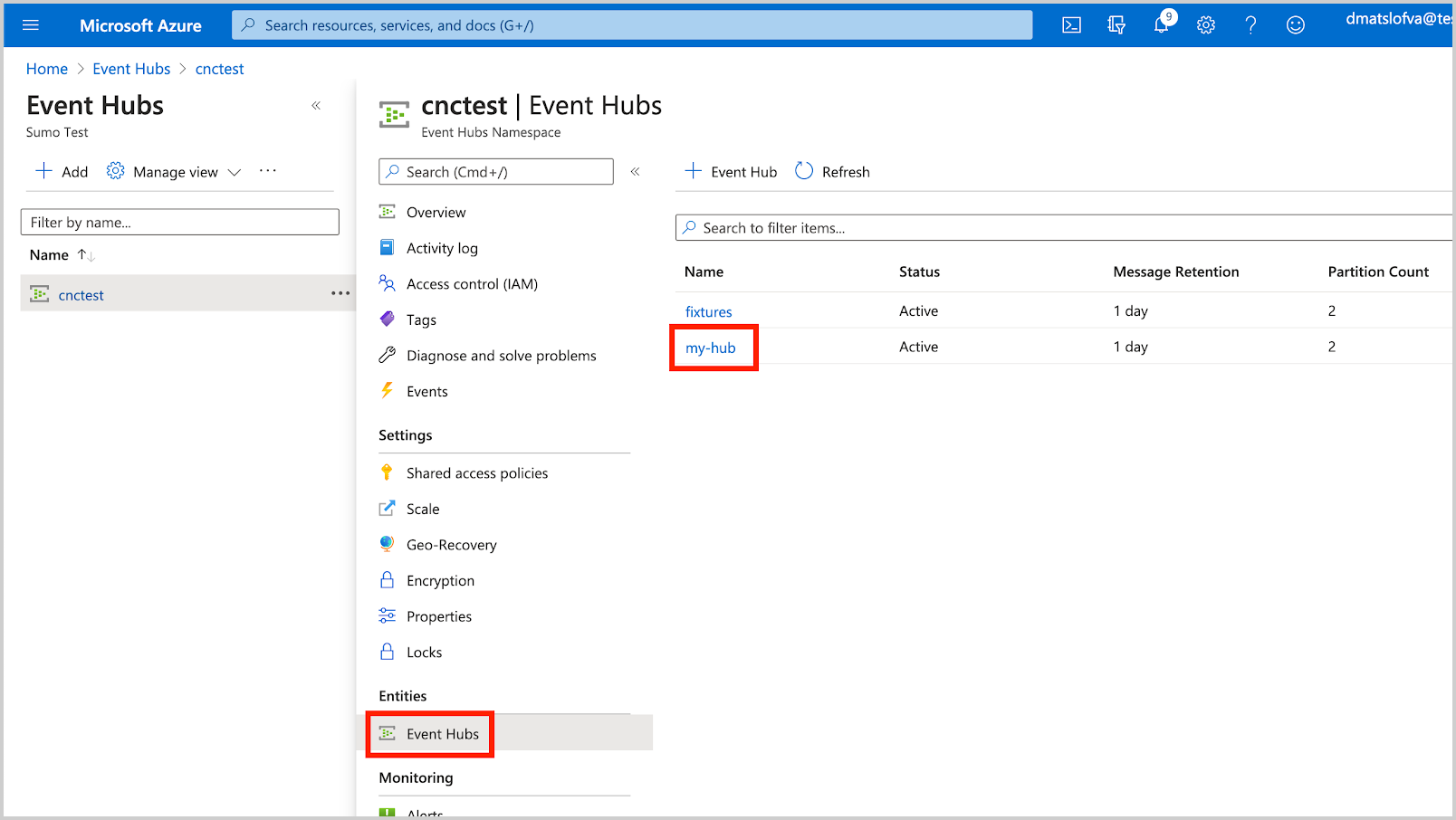
Create an Event Hub Instance.
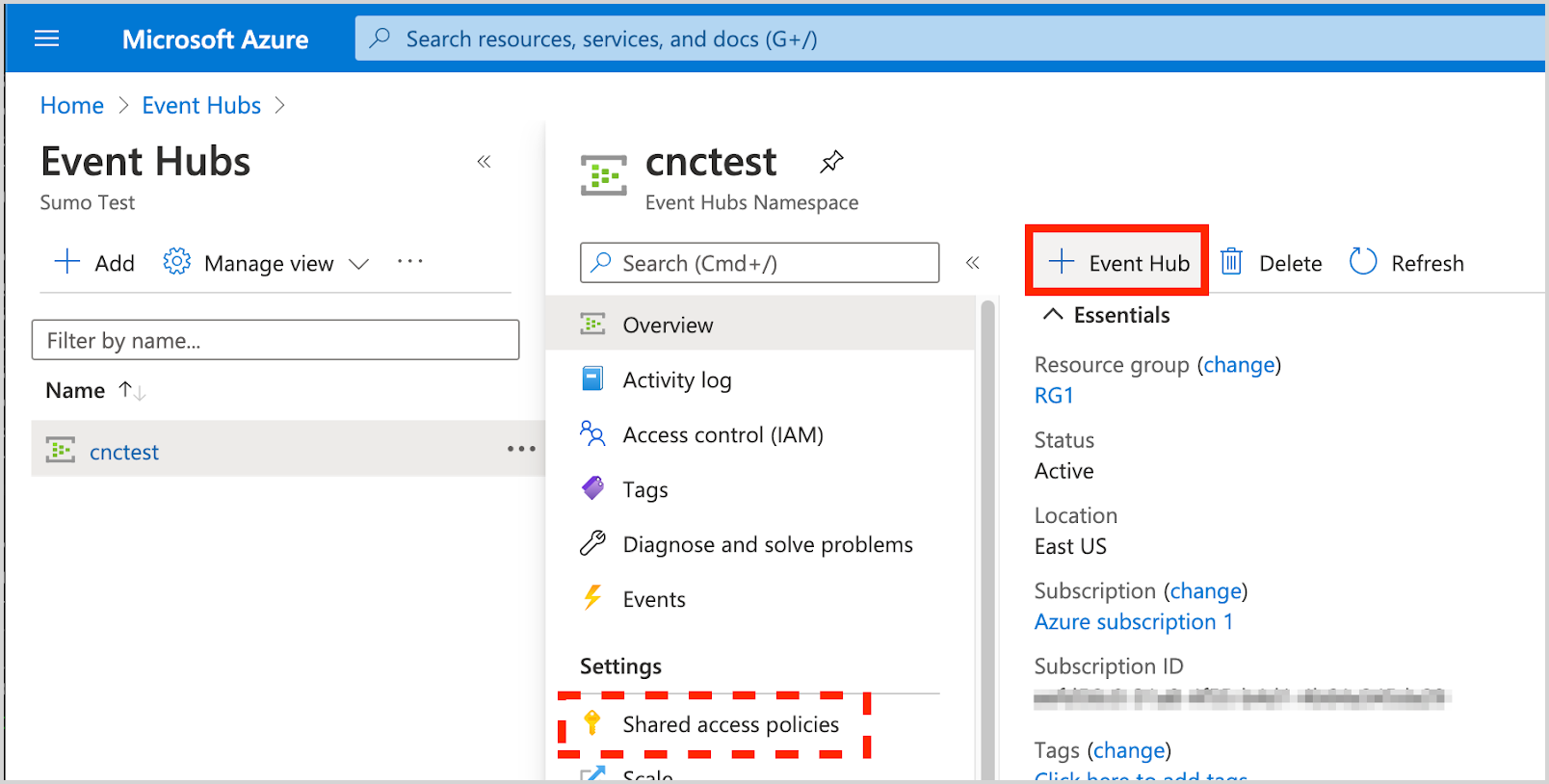
- Shared Access Policies can be set up for the entire namespace. These policies can be used to access/manage all hubs in the namespace. A policy for the namespace is created by default: RootManageSharedAccessKey
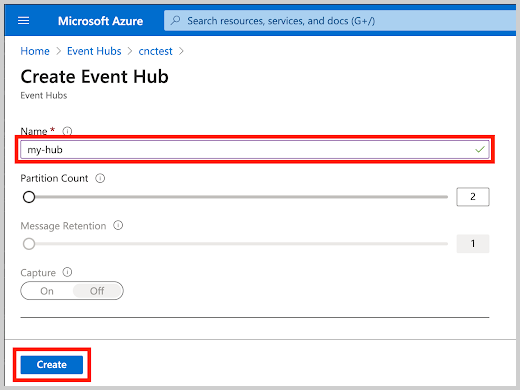 In this example, Event Hub Instance is set to my-hub.
In this example, Event Hub Instance is set to my-hub.
- Shared Access Policies can be set up for the entire namespace. These policies can be used to access/manage all hubs in the namespace. A policy for the namespace is created by default: RootManageSharedAccessKey
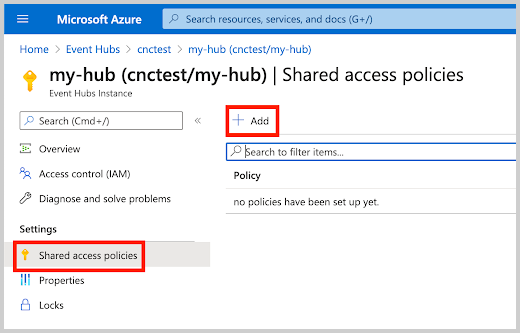
Create a Shared Access Policy with the Listen claim to the newly created Event Hub Instance:
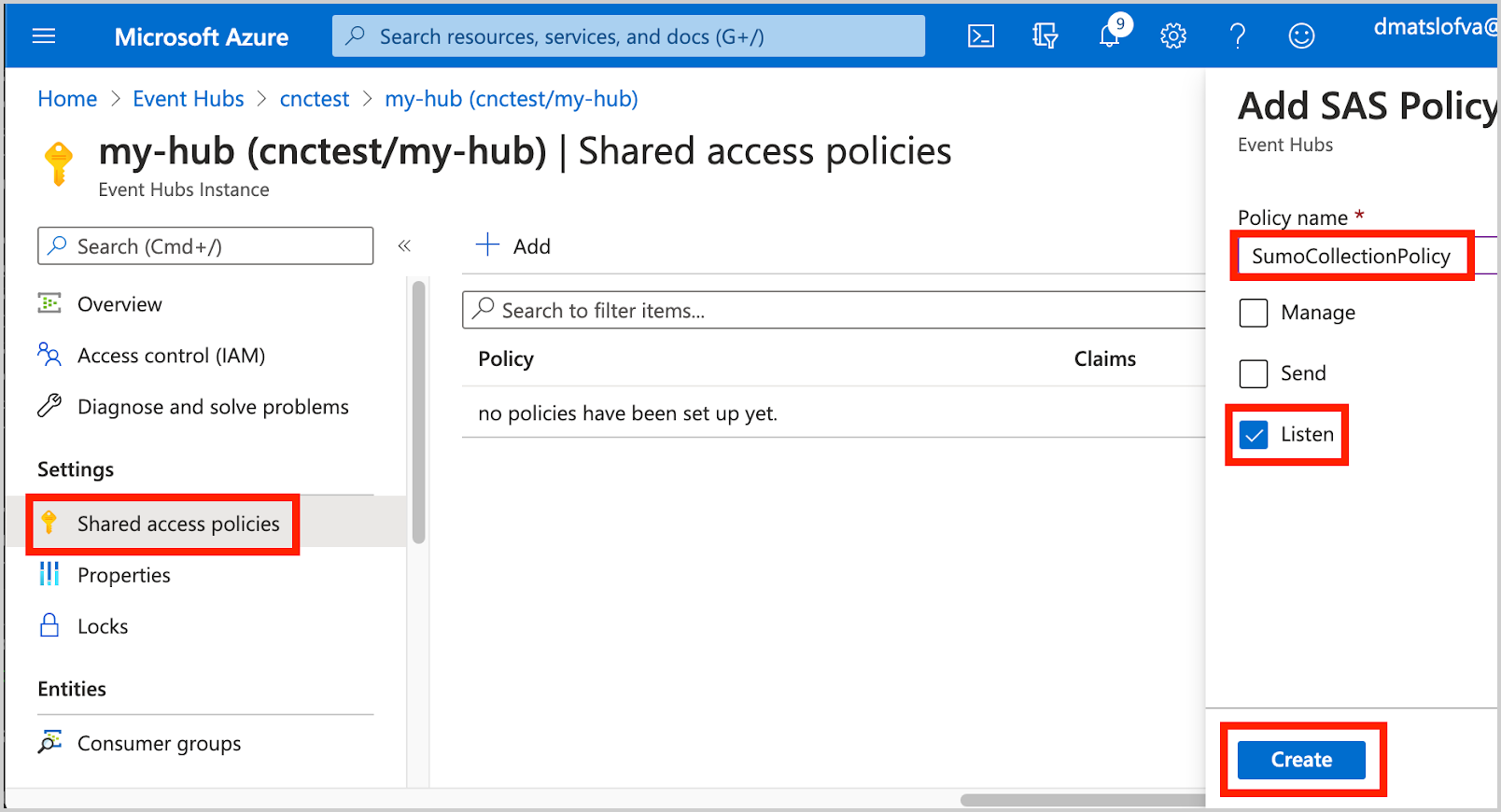
In this example, Event Hub Instance is set to SumoCollectionPolicy.Copy the Shared Access Policy Key.
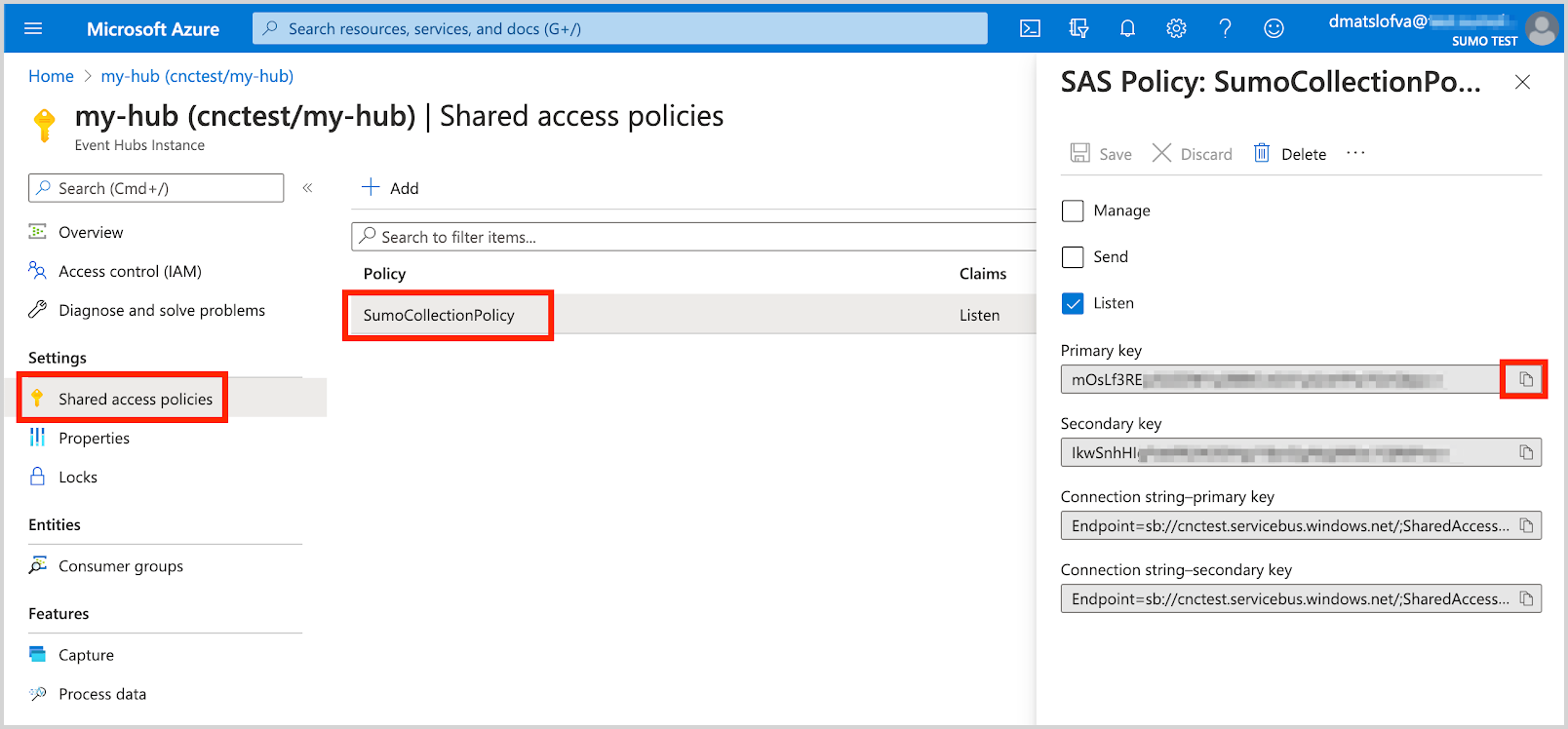 Copy the Primary/Secondary key associated with this policy.
Copy the Primary/Secondary key associated with this policy.When configuring the Azure Event Hubs Source in Sumo Logic, our input fields would be:
Field Value Azure Event Hubs Namespace cnctest Event Hubs Instance Name my-hub Shared Access Policy Name SumoCollectionPolicy Shared Access Policy Key mOsLf3RE… 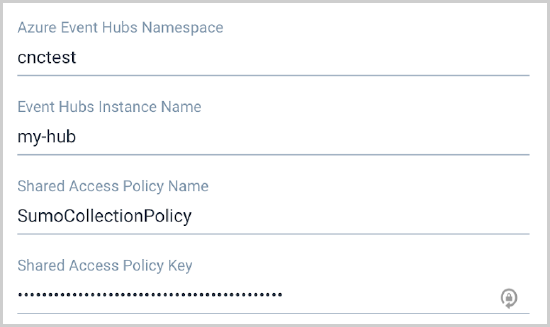
States
An Azure Event Hubs Source tracks errors, reports its health, and start-up progress. You’re informed, in real-time, if the Source is having trouble connecting, if there's an error requiring user action, or if it is healthy and collecting by utilizing Health Events.
An Azure Event Hubs Source goes through the following states when created:
- Pending. Once the Source is submitted, it is validated, stored, and placed in a Pending state.
- Started. A collection task is created on the Hosted Collector.
- Initialized. The task configuration is complete in Sumo Logic.
- Authenticated. The Source successfully authenticated with Azure Event Hubs.
- Collecting. The Source is actively collecting data from Azure Event Hubs.
If the Source has any issues during any one of these states, it is placed in an Error state.
When you delete the Source, it is placed in a Stopping state. When it has successfully stopped, it is deleted from your Hosted Collector.
On the Collection page, the Health and Status for Sources is displayed. Use Health Events to investigate issues with collection. You can click the text in the Health column, such as Error, to open the issue in Health Events to investigate.
Hover your mouse over the status icon to view a tooltip with details on the detected issue.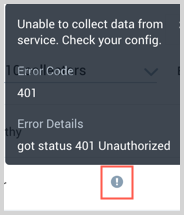
Create an Azure Event Hubs Source
When you create an Azure Event Hubs Source, you add it to a Hosted Collector. Before creating the Source, identify the Hosted Collector you want to use or create a new Hosted Collector. For instructions, see Configure a Hosted Collector.
To configure an Azure Event Hubs Source:
- In Sumo Logic, select Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
- On the Collectors page, click Add Source next to a HostedCollector.
- Select Azure Event Hubs.
- Enter a Name for the Source. The description is optional.
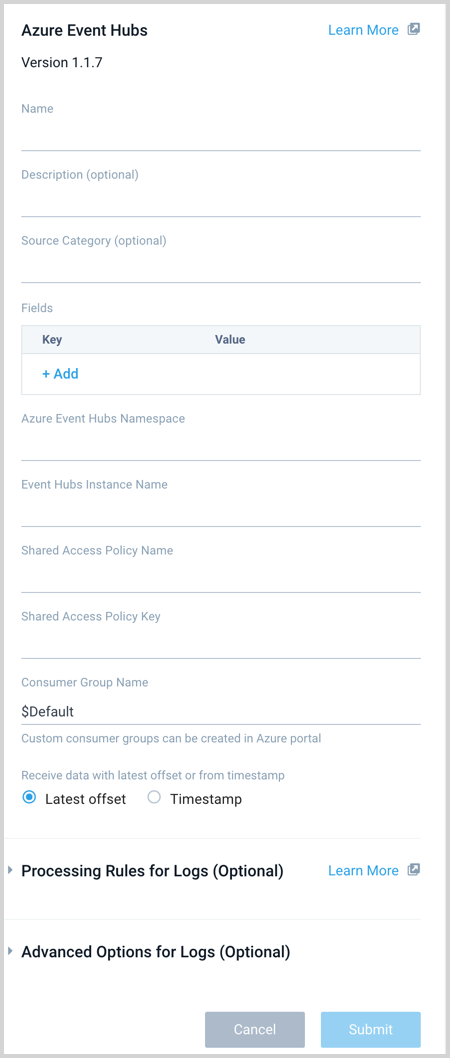
- (Optional) For Source Category, enter any string to tag the output collected from the Source. Category metadata is stored in a searchable field called
_sourceCategory. - Forward to SIEM. Check the checkbox to forward your data to Cloud SIEM Enterprise. When configured with the Forward to SIEM option the following metadata fields are set:
_siemVendor: Microsoft_siemProduct: Azure_siemFormat: JSON_siemEventID:<metadata.eventType>Wheremetadata.eventTypeis populated from the field in the event JSON, such as Administrative or Resource Health. See more information about the available event types for the Azure platform in Activity Log Categories and Resource Log Categories. Logs that do not contain a category field are assigned category UNKNOWN.
- (Optional) Fields. Click the +Add Field link to define the fields you want to associate, each field needs a name (key) and value.
A green circle with a check mark is shown when the field exists in the Fields table schema.
An orange triangle with an exclamation point is shown when the field doesn't exist in the Fields table schema. In this case, an option to automatically add the nonexistent fields to the Fields table schema is provided. If a field is sent to Sumo that does not exist in the Fields schema it is ignored, known as dropped.
- Azure Event Hubs Namespace. Enter your Azure Event Hubs Namespace name.
- Event Hubs Instance Name. Enter the Azure Event Hubs Instance Name.
- Shared Access Policy. Enter your Shared Access Policy Name and Key. The Shared Access Policy requires the Listen claim.
- Consumer Group Name. If needed, specify a custom consumer group name. When using a custom Consumer Group make sure that it exists for the Event Hub instance.
- Receive data with latest offset or from timestamp. Choose one of the following options:
- Latest offset (default) - this will start the receiver with the latest offset and collect any new logs received to the Event Hub moving forward.
- Timestamp - use this option to start receiving logs from a specific point in time in the event stream. Timestamp can be used to ingest historical data. Once all historical data has been ingested it is recommended to switch to Latest offset. This will ensure the Collector continues from the latest recorded checkpoint when restarted and not use the Timestamp specified as a starting point, which could result in logs being received and processed more than once.
- Processing Rules for Logs. Configure any desired filters, such as allowlist, denylist, hash, or mask, as described in Create a Processing Rule.
- Advanced Options for Logs.
- Timestamp Parsing. This option is selected by default. If it's deselected, no timestamp information is parsed at all.
- Time Zone. There are two options for Time Zone. You can use the time zone present in your log files, and then choose an option in case time zone information is missing from a log message. Or, you can have Sumo Logic completely disregard any time zone information present in logs by forcing a time zone. It's very important to have the proper time zone set, no matter which option you choose. If the time zone of logs can't be determined, Sumo Logic assigns logs UTC; if the rest of your logs are from another time zone your search results will be affected.
- Timestamp Format. By default, Sumo Logic will automatically detect the timestamp format of your logs. However, you can manually specify a timestamp format for a Source. See Timestamps, Time Zones, Time Ranges, and Date Formats for more information.
- When you are finished configuring the Source, click Submit.
Error types
When Sumo Logic detects an issue it is tracked by Health Events. The following table shows the three possible error types, the reason the error would occur, if the Source attempts to retry, and the name of the event log in the Health Event Index.
| Type | Reason | Retries | Retry Behavior | Health Event Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ThirdPartyConfig | Normally due to an invalid configuration. You'll need to review your Source configuration and make an update. | No retries are attempted until the Source is updated. | Not applicable | ThirdPartyConfigError |
| ThirdPartyGeneric | Normally due to an error communicating with the third party service APIs. | Yes | The Source will retry for up to 90 minutes, after which retries will be attempted every 60 minutes. | ThirdPartyGenericError |
| FirstPartyGeneric | Normally due to an error communicating with the internal Sumo Logic APIs. | Yes | The Source will retry for up to 90 minutes, after which retries will be attempted every 60 minutes. | FirstPartyGenericError |
Restarting your Source
If your Source encounters ThirdPartyConfig errors, you can restart it from either the Sumo Logic UI or Sumo Logic API.
UI
To restart your source in the Sumo Logic platform, follow the steps below:
- Open the Collection page, and go to Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
- Select the source and click the information icon on the right side of the row.
- The API usage information popup is displayed. Click the Restart Source button on the bottom left.
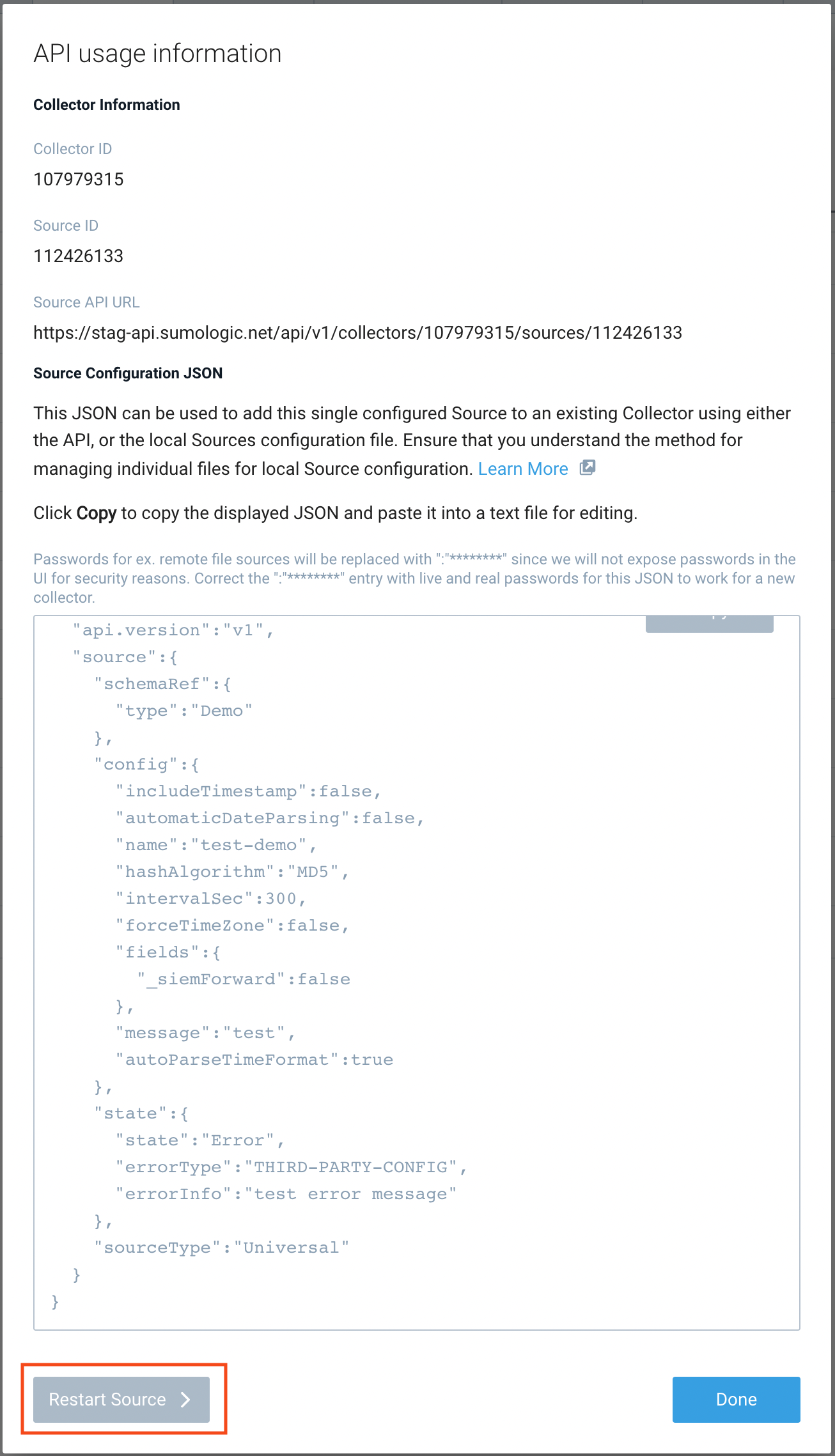
- Click Confirm to send the restart request.
- The bottom left of the platform will provide a notification informing you the request was successful.

API
To restart your source using the Sumo Management API, follow the instructions below:
- Method:
POST - Example endpoint:
https://api.sumologic.com/api/v1/collectors/{collector_id}/sources/{source_id}/action/restart
Sumo Logic endpoints like api.sumologic.com are different in deployments outside us1. For example, an API endpoint in Europe would begin api.eu.sumologic.com. A service endpoint in us2 (Western U.S.) would begin service.us2.sumologic.com. For more information, see Sumo Logic Endpoints.
JSON configuration
Sources can be configured using UTF-8 encoded JSON files with the Collector Management API. See how to use JSON to configure Sources for details.
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| config | JSON Object | Yes | Contains the configuration parameters for the Source. | |
| schemaRef | JSON Object | Yes | Use {"type":"Azure Event Hubs"} for an Azure Event Hubs Source. | not modifiable |
| sourceType | String | Yes | Use Universal for an Azure Event Hubs Source. | not modifiable |
The following table shows the config parameters for an Azure Event Hubs Source.
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
name | String | Yes | Type a desired name of the Source. The name must be unique per Collector. This value is assigned to the metadata field _source. | modifiable | |
description | String | No | null | Type a description of the Source. | modifiable |
category | String | No | null | Type a category of the source. This value is assigned to the metadata field _sourceCategory. See best practices for details. | modifiable |
fields | JSON Object | No | JSON map of key-value fields (metadata) to apply to the Collector or Source. Use the boolean field _siemForward to enable forwarding to SIEM. | modifiable | |
namespace | String | Yes | Your Azure Event Hubs Namespace name. | modifiable | |
hub_name | String | Yes | The Azure Event Hubs Instance Name | modifiable | |
access_policy_name | String | Yes | Your Shared Access Policy Name. The Shared Access Policy requires the Listen claim. | modifiable | |
access_policy_key | String | Yes | Your Shared Access Policy Key. The Shared Access Policy requires the Listen claim. | modifiable | |
consumer_group | String | Yes | $Default | If needed, specify a custom consumer group name. When using a custom Consumer Group make sure that it exists for the Event Hub instance. | modifiable |
receive_with_latest_offset | Boolean | Yes | True | Receive data with the latest offset or from the timestamp. | modifiable |
receive_from_timestamp | Boolean | No | Set to true when receive_with_latest_offset is false. | modifiable | |
timeZone | String | No | null | Type the time zone you'd like the source to use in TZ database format. Example: "America/Los_Angeles". See time zone format for details. | modifiable |
forceTimeZone | Boolean | No | false | Type true to force the Source to use a specific time zone, otherwise type false to use the time zone found in the logs. The default setting is false. | modifiable |
automaticDateParsing | Boolean | No | true | Determines if timestamp information is parsed or not. Type true to enable automatic parsing of dates (the default setting); type false to disable. If disabled, no timestamp information is parsed at all. | modifiable |
autoParseTimeFormat | Boolean | No | true | Sets if the timestamp format is automatically detected by Sumo Logic. If autoParseTimeFormat is set to false, then defaultDateFormats must be specified. | modifiable |
defaultDateFormats | Object | array | No | null | Define formats for the dates present in your log messages. You can specify a locator regex to identify where timestamps appear in log lines. The defaultDateFormats object has two elements:format (required)—Specify the date format.locator (optional)—A regular expression that specifies the location of the timestamp in your log lines. For example, INFO(.*)For an example, see Timestamp example, below. For more information about timestamp options, see Timestamps, Time Zones, Time Ranges, and Date Formats. |
Azure Event Hubs Source JSON example:
{
"api.version": "v1",
"source": {
"schemaRef": {
"type": "Azure Event Hubs"
},
"config": {
"name": "Azure Event Hubs",
"description": "East field",
"namespace": "namespace",
"hub_name": "hub name",
"access_policy_name": "policyName",
"access_policy_key": "********",
"consumer_group": "groupName",
"fields": {
"_siemForward": false
},
"category": "eastTeamF",
"receive_with_latest_offset": true,
"automaticDateParsing": true,
"autoParseTimeFormat": false,
"defaultDateFormats": [{
"format": "dd-MM-yyyy",
"locator": "INFO(.*)"
}]
},
"sourceType": "Universal"
}
}