Cisco Meraki Source
The Cisco Meraki Source provides a secure endpoint to receive data from the Meraki organization and networks and ingests event logs pertaining to them. It securely stores the required authentication, scheduling, and state tracking information.
Data Sources
| Default Interval | API Endpoint |
|---|---|
| Every 24 Hours | Get Organizations |
| Every 24 Hours | Get Organization Networks |
| Every 15 Minutes | Get Organization Appliance Security Events |
| Every 15 Minutes | Get Organization Configuration Changes |
| Every 15 Minutes | Get Network Events |
| Every 15 Minutes | Get Network Wireless Air Marshal |
States
A Cisco Meraki Source tracks errors, reports its health, and start-up progress. You’re informed, in real-time, if the Source is having trouble connecting, if there's an error requiring user action, or if it is healthy and collecting by utilizing Health Events.
- Pending. Once the Source is submitted, it is validated, stored, and placed in a Pending state.
- Started. A collection task is created on the Hosted Collector.
- Initialized. The task configuration is complete in Sumo Logic.
- Authenticated. The Source successfully authenticated with Meraki.
- Collecting. The Source is actively collecting data from Meraki.
If the Source has any issues during any one of these states, it is placed in an Error state.
When you delete the Source, it is placed in a Stopping state. When it has successfully stopped, it is deleted from your Hosted Collector. On the Collection page, the Health and Status for Sources is displayed. Use Health Events to investigate issues with collection. You can click the text in the Health column, such as Error, to open the issue in Health Events to investigate.
Hover your mouse over the status icon to view a tooltip with details on the detected issue.
Setup and Configuration
In this configuration, you will set up an Meraki source account and configure it to be authorized and authenticated to use device logs and alerts from MERAKI API. To obtain an Meraki auth token, follow the steps below:
- Log in to the Meraki application.
- Navigate to the Organization, under Configure section, select Settings page.
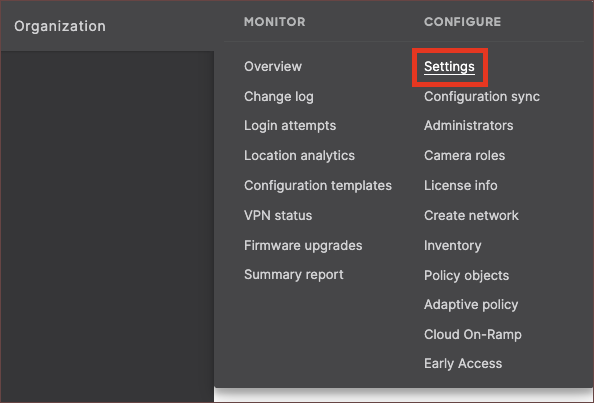
- Check the Enable access to the Cisco Meraki Dashboard API

- Click Save Changes at the bottom of the page.
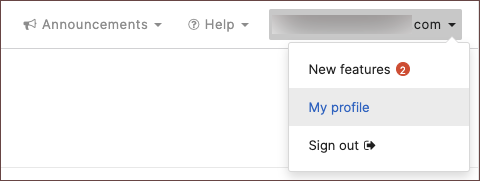
- Navigate to your profile by clicking your name in the upper right corner and select My profile.
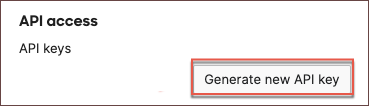
- Scroll down to API access and click Generate new API key.
- Save your new API key into your preferred password vault for later use.
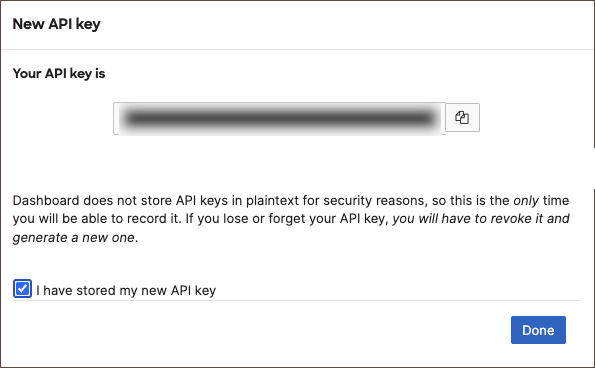
For more detailed steps with troubleshooting examples, visit the official documentation here.
Gather Meraki Organization IDs
You will need to provide a single Meraki organization identifier in the configuration. Run the following curl command using your Cisco Meraki API key to see the list of Meraki organizations and note the ID number for the organizations you wish to collect data from.
curl --location 'https://api.meraki.com/api/v1/organizations' --header 'Authorization: Bearer {{api_key}}'
Create a Cisco Meraki Source
When you create an Cisco Meraki Source, you add it to a Hosted Collector. Before creating the Source, identify the Hosted Collector you want to use or create a new Hosted Collector. For instructions, see Configure a Hosted Collector. You will need to create a new Cisco Meraki source for every Cisco Meraki organization you want to collect data from.
To configure Cisco Meraki Source:
- In Sumo Logic, select Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
- On the Collectors page, click Add Source next to a Hosted Collector.
- Select Cisco Meraki.

- Enter a Name to display for the Source in the Sumo Logic web application. The description is optional.
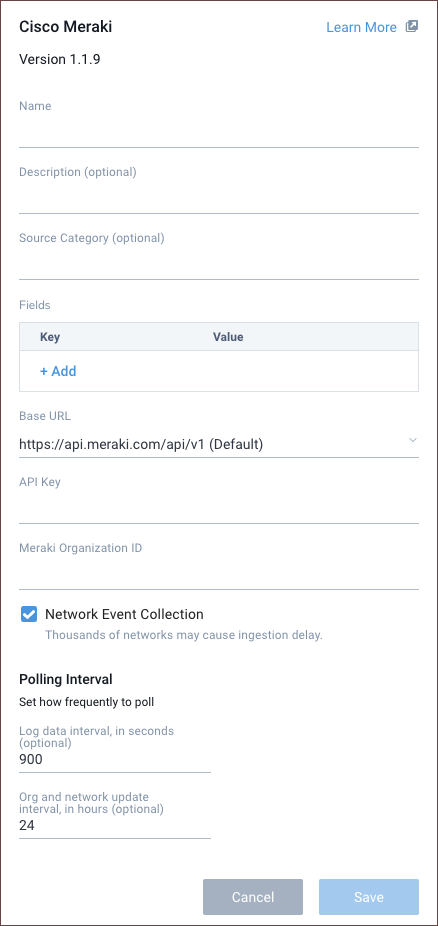
- (Optional) For Source Category, enter any string to tag the output collected from the Source. Category metadata is stored in a searchable field called
_sourceCategory. - (Optional) Fields. Click the +Add Field link to define the fields you want to associate. Each field needs a name (key) and value.
A green circle with a checkmark is shown when the field exists in the Fields table schema.
An orange triangle with an exclamation point is shown when the field doesn't exist in the Fields table schema. In this case, an option to automatically add the nonexistent fields to the Fields table schema is provided. If a field is sent to Sumo Logic that does not exist in the Fields schema it is ignored (i.e., dropped).
- Base URL. It refers to the default URL where your Meraki account is hosted. If you are located in China, you have the option to modify the base URL.
- API Key. Provide the API key you generated from your Meraki account.
- Meraki Organization ID. Provide the numeric Meraki organization ID of the Meraki org you want to collect data from. You can only provide one ID. Please create multiple sources for multiple Meraki organizations.
- Network Event Collection. Enable or disable this option to collect information about your Meraki Networks, their network events, and wireless Air Marshal events.
- (Optional) The Polling Interval is set to 300 seconds by default, you can adjust it based on your needs.
- When you are finished configuring the Source, click Save.
Error types
When Sumo Logic detects an issue it is tracked by Health Events. The following table shows the three possible error types, the reason the error would occur, if the Source attempts to retry, and the name of the event log in the Health Event Index.
| Type | Reason | Retries | Retry Behavior | Health Event Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ThirdPartyConfig | Normally due to an invalid configuration. You'll need to review your Source configuration and make an update. | No retries are attempted until the Source is updated. | Not applicable | ThirdPartyConfigError |
| ThirdPartyGeneric | Normally due to an error communicating with the third-party service APIs. | Yes | The Source will retry for up to 90 minutes, after which it quits. | ThirdPartyGenericError |
| FirstPartyGeneric | Normally due to an error communicating with the internal Sumo Logic APIs. | Yes | The Source will retry for up to 90 minutes, after which it quits. | FirstPartyGenericError |
Restarting your Source
If your Source encounters ThirdPartyConfig errors, you can restart it from either the Sumo Logic UI or Sumo Logic API.
UI
To restart your source in the Sumo Logic platform, follow the steps below:
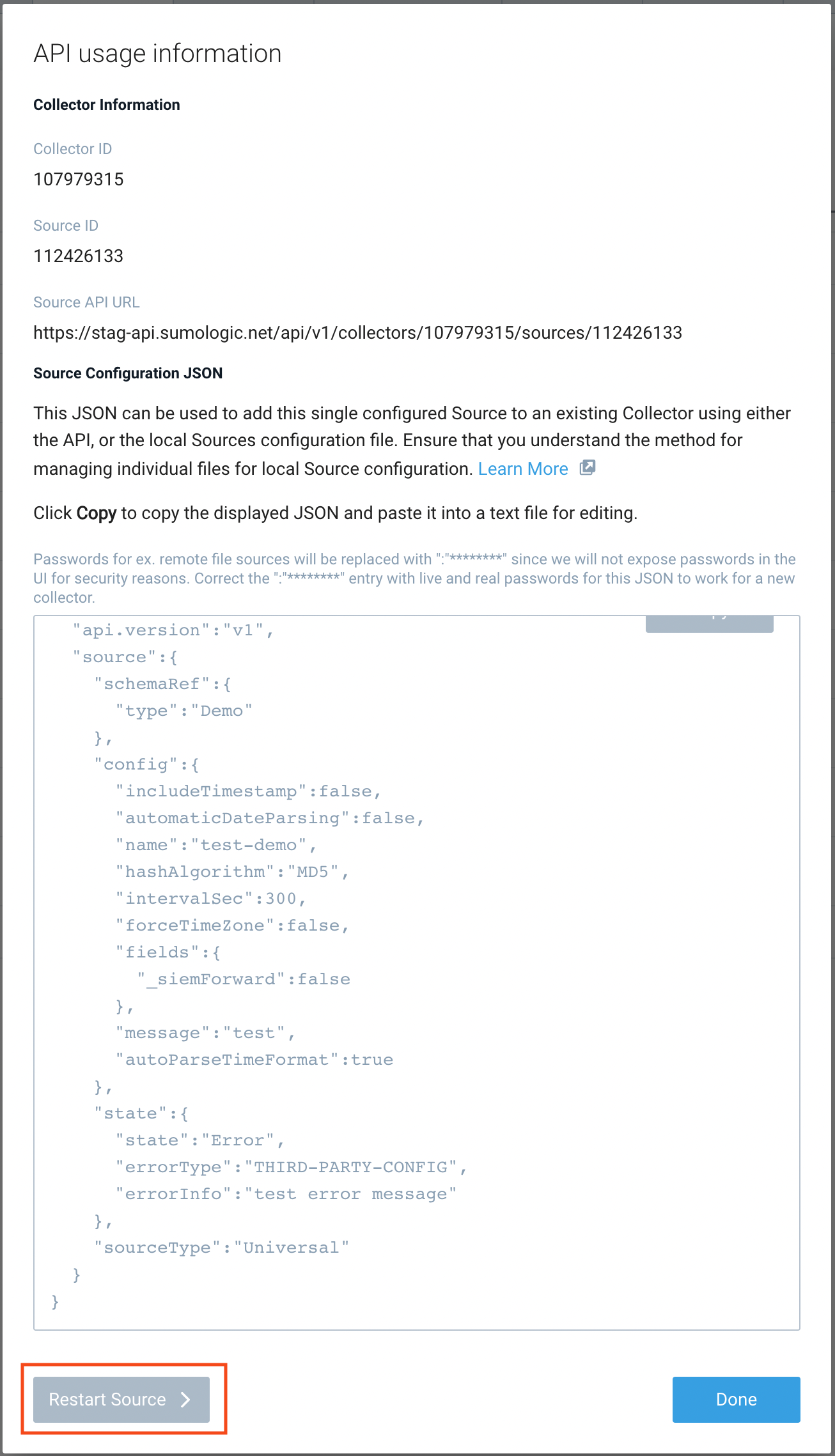
- Open the Collection page, and go to Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
- Select the source and click the information icon on the right side of the row.
- The API usage information popup is displayed. Click the Restart Source button on the bottom left.
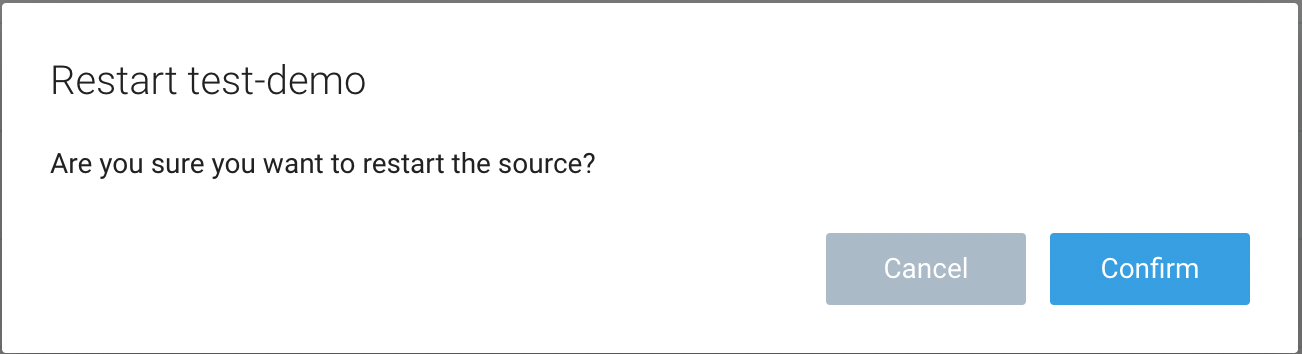
- Click Confirm to send the restart request.
- The bottom left of the platform will provide a notification informing you the request was successful.

API
To restart your source using the Sumo Management API, follow the instructions below:
- Method:
POST - Example endpoint:
https://api.sumologic.com/api/v1/collectors/{collector_id}/sources/{source_id}/action/restart
Sumo Logic endpoints like api.sumologic.com are different in deployments outside us1. For example, an API endpoint in Europe would begin api.eu.sumologic.com. A service endpoint in us2 (Western U.S.) would begin service.us2.sumologic.com. For more information, see Sumo Logic Endpoints.
JSON configuration
Sources can be configured using UTF-8 encoded JSON files with the Collector Management API. See how to use JSON to configure Sources for details.
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
config | JSON Object | Yes | Contains the configuration-parameters of the Source. | |
schemaRef | JSON Object | Yes | Use {"type":"Cisco Meraki"} for Cisco Meraki Source. | not modifiable |
sourceType | String | Yes | Use Universal for Cisco Meraki Source. | not modifiable |
Config Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
name | String | Yes | Type the desired name of the Source and it must be unique per Collector. This value is assigned to the metadata field _source. | modifiable |
description | String | No | Type the description of the Source. | modifiable |
category | String | No | Type the category of the source. This value is assigned to the metadata field _sourceCategory. | modifiable |
fields | JSON Object | No | JSON map of key-value fields (metadata) to apply to the Collector or Source. Use the boolean field _siemForward to enable forwarding to SIEM. | modifiable |
baseURL | String | Yes | Region URL of the Cisco Meraki application. | modifiable |
apiSecretKey | String | Yes | Cisco Meraki API secret key | modifiable |
merakiOrg | String | Yes | Cisco Meraki Organization ID | modifiable |
pollingInterval | Integer | No | 300 | This sets how often the Source checks for new data. |
Troubleshooting
You may receive the follow error below if you enter an invalid Cisco Meraki organization ID in your configuration. Please follow the steps in the section Gather Meraki Organization IDs to ensure you are using an ID for a Meraki organization returned in that query.
{
"state": "Error",
"errorType": "THIRD-PARTY-CONFIG",
"errorCode": 400,
"errorInfo": "meraki '/api/v1/organizations/orgIdInput' not found using API key"
}
Known Issues
- Pagination has a rare occurrence to potentially return a small number duplicate logs. This issue has been reported to Cisco.
- The Cisco Meraki API has a rate limit of 10 API calls every second. There is a possibility for the source to have a collection delay if your Meraki organization has thousands of networks with many product types. The Cisco Meraki API for collecting network events requires we make one API call per network, per product type. There are a total of 6 product types. The API also requires one API call per network for collecting wireless Air Marshal events. This means 2,000 networks can be around 14,000 API calls (2000*6+2000) to retrieve network events assuming no pagination is needed. At the rate limit of 10 API calls per second, the quickest we could make API calls is around 24 mins. Occasionally the Cisco Meraki API can take around 1 to 2 seconds to respond adding to the time. In order to solve this issue, Cisco would need to raise the API rate limit or provide an API endpoint for collecting network events and wireless Air Marshal events without the requirement to iterate over each network and product type individually.