Collect Logs from AWS Fargate
This page describes how to collect logs from AWS Fargate.
Collection process
The diagram below illustrates the process for sending container logs from AWS Fargate to Sumo Logic.
AWS Fargate uses the AWSLogs driver to send container logs to AWS CloudWatch.
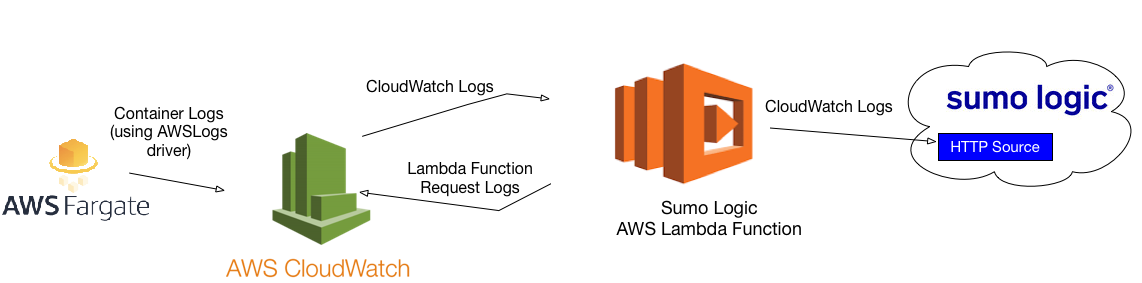
Collecting CloudWatch logs
First, configure containers for CloudWatch logging by following the instructions in Create a Task Definition in Amazon help. When creating your Task Definition, be sure to configure the logging to use the awsLogs driver, by setting the logConfiguration parameter to "awslogs", currently the only logging driver supported by AWS Fargate.
We recommend collecting Amazon CloudWatch Logs using our AWS Lambda function to subscribe to your CloudWatch Log Group. Our AWS Lambda function converts the CloudWatch log format into a format that is compatible with Sumo, then POSTs the data directly to a Sumo HTTP Source. This is the preferred method for the following types of data that are delivered through Amazon CloudWatch Logs:
- Custom CloudWatch log data. The AWS Lambda function should handle any log data. However, you should make sure to test this with your actual data, to ensure that unusually formatted logs are parsed correctly.
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs. The AWS Lambda function is compatible with the Sumo Amazon VPC Flow Logs App.
- AWS Lambda logs. The AWS Lambda function is built for logs generated by your AWS Lambda functions and is compatible with our Sumo AWS Lambda App.
Collect CloudWatch Logs using a CloudFormation Template
This section has instructions for creating AWS resources using a Sumo-provided CloudFormation template. The template specifies the resources necessary to send Amazon CloudWatch Logs to Sumo, including a Lambda function for sending logs, another Lambda function configured with a dead letter queue for resending messages as necessary, and associated roles and permissions. For more information about the resources created, see Download the CloudFormation template.
CloudFormation based approach is recommended. If you would rather manually configure a Lambda function see Collect Amazon CloudWatch Logs with Lambda Function.
AWS Lambda functions are our preferred method for sending Amazon CloudWatch Logs to Sumo, but there are alternative methods: Amazon Kinesis, or a collector script. See Alternate Collection Methods below.
Add a Hosted Collector and HTTP Source
- In Sumo Logic, configure a Hosted Collector.
- In Sumo Logic, configure an HTTP Source.
When you configure the HTTP Source, make sure to save the HTTP Source Address URL. You will need this to configure the Lambda Function.
Download the CloudFormation template
If you want to make any of the optional modifications described in this section, download the DLQLambdaCloudFormation.json CloudFormation template from https://s3.amazonaws.com/appdev-cloudformation-templates/DLQLambdaCloudFormation.json. Otherwise, proceed to Create a stack on the AWS CloudFormation console.
When you upload the template to AWS, it creates the AWS resources described in the table below.
| Resource Name | Description |
|---|---|
SumoCWLogGroup | A log group that has a subscription filter (SumoCWLogSubsriptionFilter) associated with it that delivers real time logs to Sumo’s CloudWatch Lambda function (SumoCWLogsLambda). |
SumoCWLogsLambda | A Lambda function responsible for sending data to the Sumo HTTP Source URL. It is configured with a dead letter queue (SumoCWDeadLetterQueue) that receives messages that can’t be processed successfully. You can subscribe other logs to this function except its own log group. |
SumoCWProcessDLQLambda | A Lambda function responsible for reading messages from the dead letter queue and resending messages. This function is periodically triggered by AWS CloudWatch Events using a schedule rule (SumoCWProcessDLQScheduleRule). |
SumoCWLambdaPermission | Permission to CloudWatch Logs for invoking Lambda functions. |
SumoCWLambdaExecutionRole | IAM Role for the two Lambda functions. The role includes policies for creating CloudWatch Logs, running CRUD operations on the dead letter queue (SumoCWDeadLetterQueue), and invoking Lambda functions. |
SumoCWEventsInvokeLambdaPermission | Permission for CloudWatch events to trigger the SumoCWProcessDLQLambda Lambda function. |
SumoCWSpilloverAlarm | An alarm that is triggered if the number of messages in the Dead Letter Queue exceeds the threshold defined in the CoudFormation template (default is 100000). The alarm is configured with a “send email” action (SumoCWEmailSNSTopic). You must verify receipt of emails sent to the email endpoint defined in CloudFormation template. |
Tailor the CloudFormation template
Before you upload the CloudFormation template, there are some optional configuration steps.
If you want to use the CloudFormation Template as is, proceed to Create a stack on the AWS CloudFormation console.
Configure environment variables for Lambda functions
The following AWS Lambda environment variables are supported in both the Lambda functions. Both the functions should have same environment variables values configured to avoid inconsistencies.
| Environment Variable | Description |
|---|---|
SOURCE_CATEGORY_OVERRIDE | (Optional) You can use this variable to override the _sourceCategory configured for the HTTP Source. |
SOURCE_FIELDS_OVERRIDE | (Optional) You can use this variable to override the custom metadata fields configured for the HTTP Source. Example: key1=value1,key2=value2 |
SOURCE_HOST_OVERRIDE | (Optional) You can use this variable to override the _sourceHost configured for the HTTP Source. |
SOURCE_NAME_OVERRIDE | (Optional) You can use this variable to override the _sourceName configured for the HTTP Source. |
If you are configuring log collection for VPC flow logs, see the Environment variables for VPC flow log collection section on Collect Amazon VPC Flow Logs from CloudWatch using CloudFormation.
Define variables in the Environment section of the Cloud Formation template.
"Environment": {
"Variables": {
“SOURCE_CATEGORY_OVERRIDE”: "<insert-value-here>"
“SOURCE_HOST_OVERRIDE”: "<insert-value-here>"
“SOURCE_NAME_OVERRIDE”: "<insert-value-here>"
“SOURCE_FIELDS_OVERRIDE”: "<insert-value-here>"
}
}
Configure threshold for DeadLetterQueue
If you don’t want to use the SumoCWSpilloverAlarm, as described below in Remove alarm resources, you can skip this step.
In the CloudFormation template, define the number of messages in the Dead Letter Queue that will trigger the SumoCWSpilloverAlarm, using the Threshold attribute in the alarm definition.
"SumoCWSpilloverAlarm":{
"Type":"AWS::CloudWatch::Alarm",
"Properties":{
"AlarmActions":[
{
"Ref":"SumoCWEmailSNSTopic"
}
],
"AlarmDescription":"Notify via email if number of messages in DeadLetterQueue exceeds threshold",
"ComparisonOperator":"GreaterThanThreshold",
"Dimensions":[
{
"Name": "QueueName",
"Value": "SumoCWDeadLetterQueue"
}
],
"EvaluationPeriods":"1",
"MetricName":"ApproximateNumberOfMessagesVisible",
"Namespace":"AWS/SQS",
"Period":"3600",
"Statistic":"Sum",
"Threshold":"100000"
},
"DependsOn": ["SumoCWEmailSNSTopic"]
Remove alarm resources
(Optional) If you do not want the SumoCWSpilloverAlarm alarm to be created, remove the definitions of the SumoCWEmailSNSTopic and SumoCWSpilloverAlarm resources from the CloudFormation template. Delete the sections shown below.
"SumoCWEmailSNSTopic": {
"Type":"AWS::SNS::Topic",
"Properties":{
"Subscription":[ {
"Endpoint" : "hpal@sumologic.com",
"Protocol" : "email"
}]
}
},
"SumoCWSpilloverAlarm":{
"Type":"AWS::CloudWatch::Alarm",
"Properties":{
"AlarmActions":[
{
"Ref":"SumoCWEmailSNSTopic"
}
],
"AlarmDescription":"Notify via email if number of messages in DeadLetterQueue exceeds threshold",
"ComparisonOperator":"GreaterThanThreshold",
"Dimensions":[
{
"Name": "QueueName",
"Value": "SumoCWDeadLetterQueue"
}
],
"EvaluationPeriods":"1",
"MetricName":"ApproximateNumberOfMessagesVisible",
"Namespace":"AWS/SQS",
"Period":"3600",
"Statistic":"Sum",
"Threshold":"100000"
},
"DependsOn": ["SumoCWEmailSNSTopic"]
}
Create a stack on the AWS CloudFormation console
- Log in to the AWS Management Console.
- Under Management Tools, select CloudFormation.
- Create a new stack by clicking Create Stack, then select “With new resources (standard).”
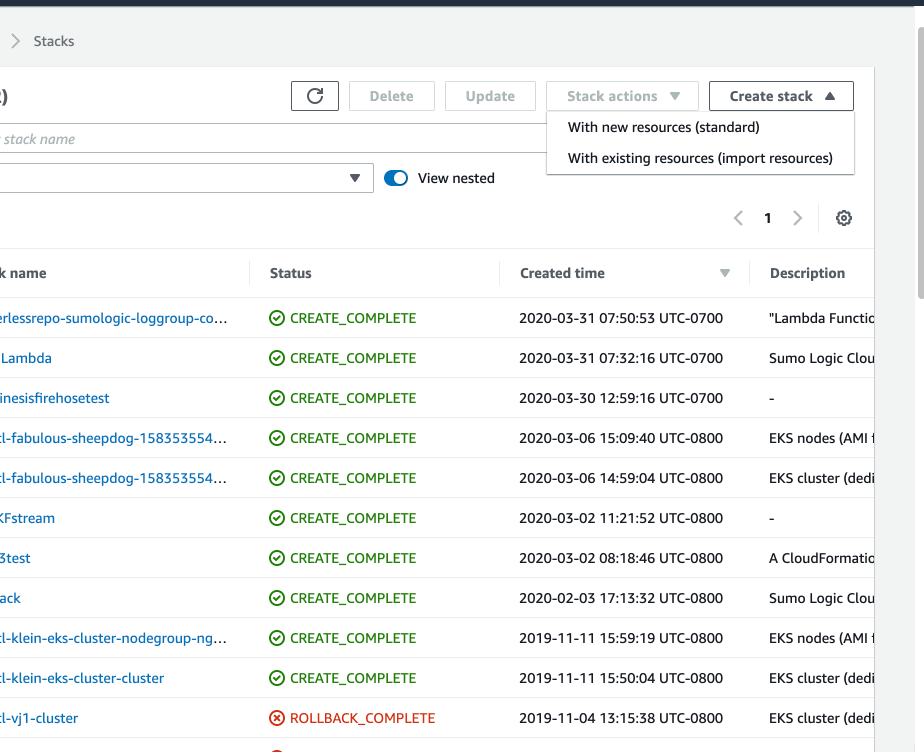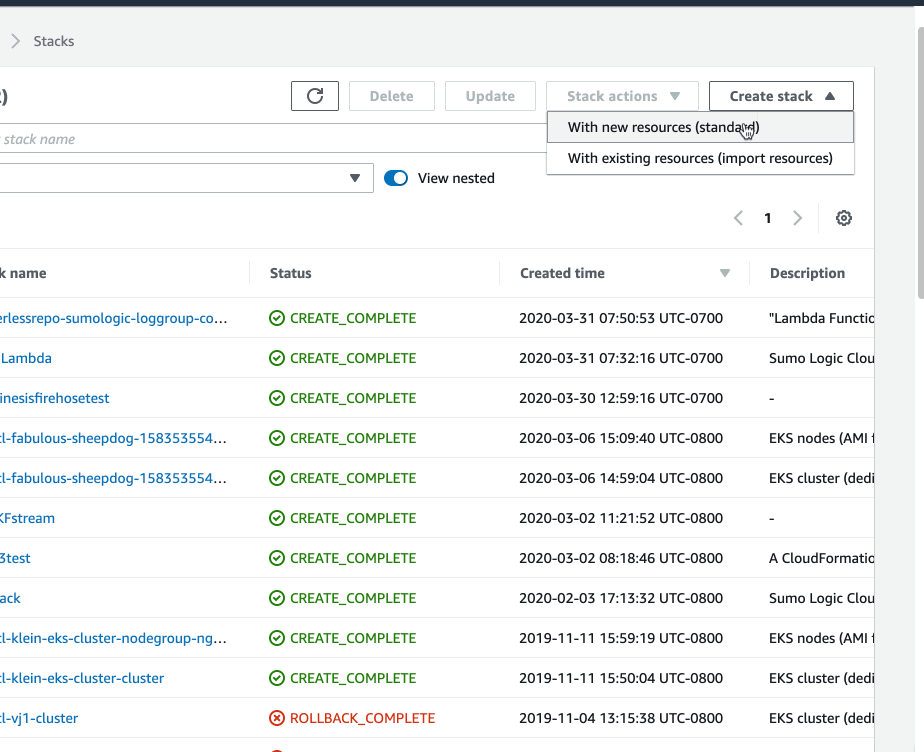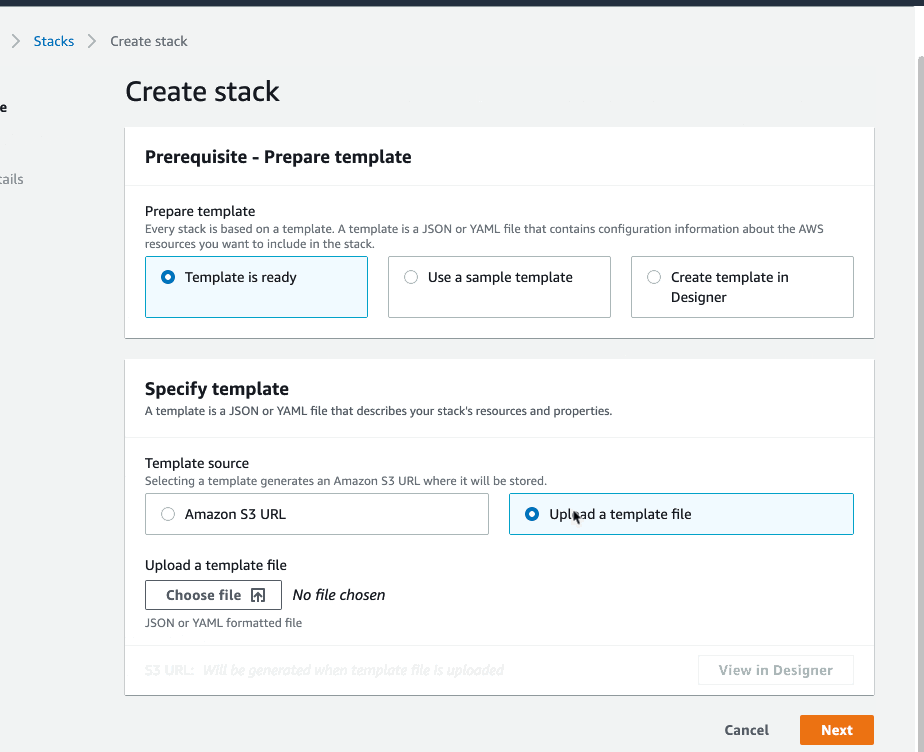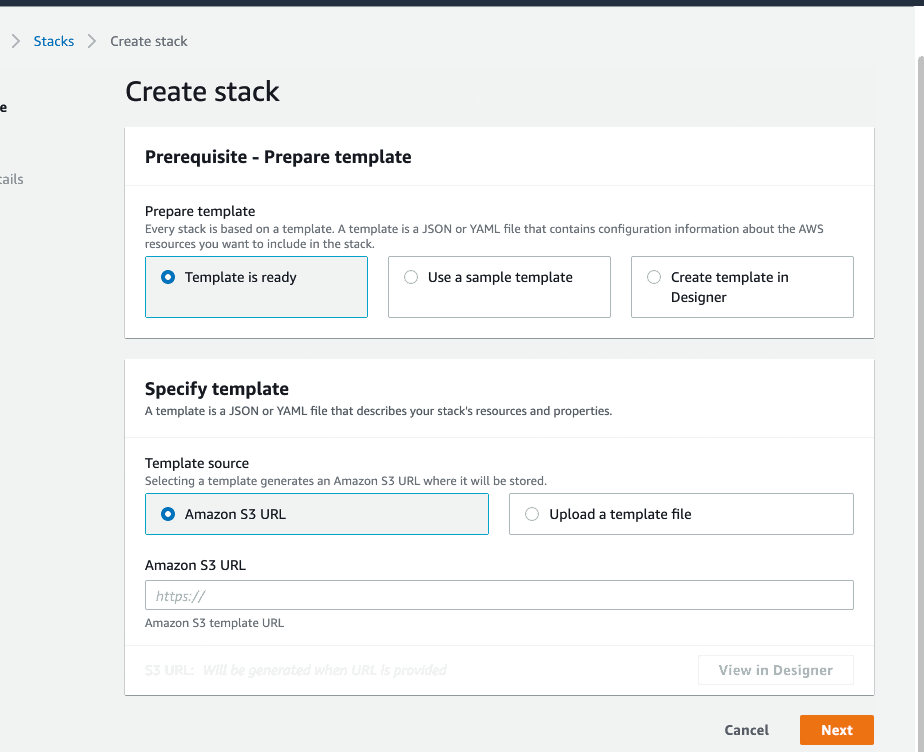
On the Specify Template window, do one of the following:
If you have downloaded and optionally modified the CloudFormation template, choose to Upload a template file, upload the
DLQLambdaCloudFormation.jsonfile, and then click Next.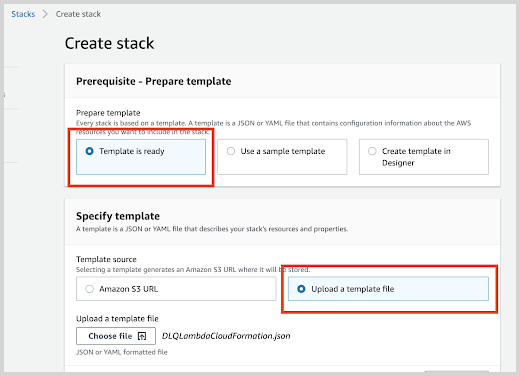
Otherwise, if you did not modify the CloudFormation template, select Specify an Amazon S3 template URL and enter:
https://s3.amazonaws.com/appdev-cloudformation-templates/DLQLambdaCloudFormation.json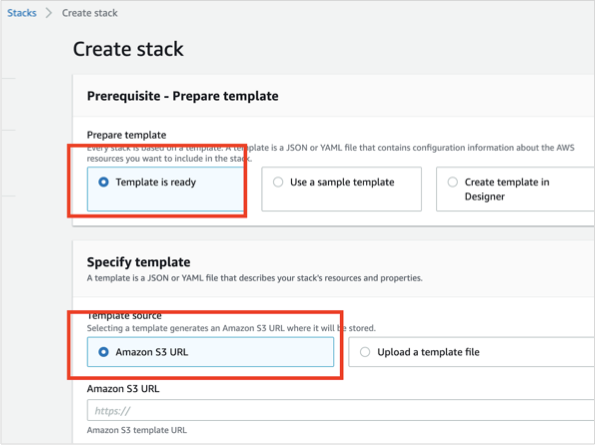
Select Next and the Specify Stack Details window appears. Enter the following:
Stack Name.
EmailID (Optional) Used for alerts.
IncludeLogGroupInfo. Set to true to include loggroup/logstream values in logs. The default value is False. For AWS Lambda Logs IncludeLogGroupInfo must be set to True; for VPC Flow Logs it's optional.
LogFormat. For VPC logs, choose either VPC-JSON (JSON format) or VPC-RAW (raw messages). The default value is Others.
LogStreamPrefix (Optional) Enter comma separated list of logStream name prefixes to filter by logStream. Please note this is separate from a logGroup. This is used to only send certain logStreams within a CloudWatch logGroup(s). LogGroup(s) still need to be subscribed to the created Lambda function (
SumoCWLogsLambda-<Auto-Genereted-Suffix>), regardless of what is input for this value.noteLogStreamPrefix field does not accept special characters (
[|\\{}()[\]^$+*?.-]). For example, you can use the comma-separated list like test-name, test-logs as the LogStream name prefixes.NumOfWorkers. (Optional) Increase this value to speed up dead letter queue (DLQ) processing.
SumoEndPointURL (Required). Enter the HTTP Source Address URL from Add a Hosted Collector and HTTP Source.
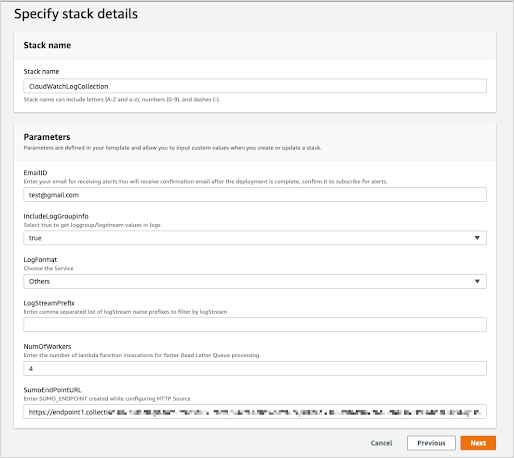
Click Next. The Configure Stack Options screen will appear. You can optionally add AWS tags to tag the resources created by this Cloudformation stack. Click Next to get to the final Review window.
In the Review window, click the checkbox acknowledging that you understand the the template creates IAM resources, and click Create.
After few minutes you will see CREATE_COMPLETE in the Status column.
If you're using an existing log group or if you don’t want to send logs to the default group SumoCWLogGroup then you must do one of the following: Manually subscribe the SumoCWLogsLambda to an existing CloudWatch Log Group, create a subscription filter manually, or Auto-Subscribe AWS Log Groups to a Lambda Function.
Validate email address for alarms
Log in to the email account whose address you provided when performing the configuration described in Create a stack on the AWS CloudFormation console above. Look for an email with subject "AWS Notification - Subscription Confirmation", like the example shown below.
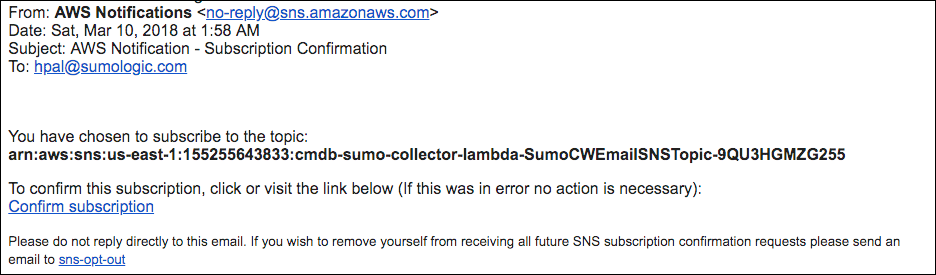
To validate the email address, click Confirm subscription in the email.
Dealing with alarms
If you receive an alarm email like the one shown in the previous section, the number of messages in the dead letter queue exceeds the threshold defined in the CloudFormation template, which by default is 100,000. This could be because:
SumoCWProcessDLQLambdamay not be able to process messages as quickly as the messages are received. In this case, you may want to use the Lambda console to increase the number of workers specified by theNUM_OF_WORKERSenvironment variable.SumoCWProcessDLQLambdamay be unable process incoming messages because of an error in the message format or a configuration problem, for example, an error in the HTTP endpoint configuration. Test the function with the message in the Lambda console to see whether it is able to process the message and send it to Sumo.
Subscribe SumoCWLogsLambda to CloudWatch Log Groups
The procedure described above subscribes a single Log Group, SumoCWLogGroup, to the SumoCWLogsLambda function. If you would like to subscribe additional CloudWatch Log Groups to the SumoCWLogsLambda function, follow the instructions in the sections below.
Manually subscribe SumoCWLogsLambda to an existing CloudWatch Log Group
If you only need to collect logs from a few additional CloudWatch Log groups, you can manually subscribe the SumoCWLogsLambda function to an existing CloudWatch Log Group using the instructions below.
Log in to the AWS Management Console.
Under Management Tools, select CloudWatch, then click Logs in the left- hand navigation menu.
Select the radio button next to the CloudWatch Log Group that you want to stream to Sumo Logic, click Actions, then click Stream to AWS Lambda.
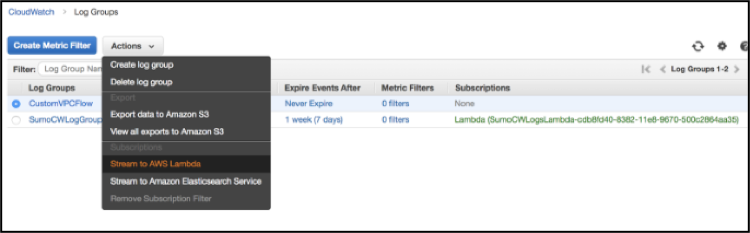
Select the Lambda function that begins with "SumoCWLogsLambda", then click Next.
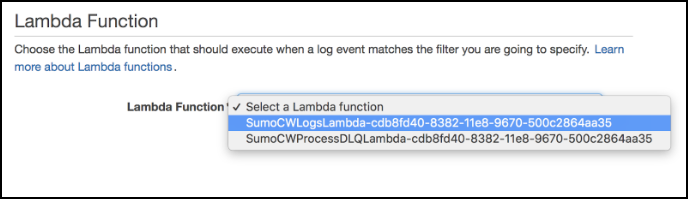
Select the appropriate log format, then click Next.
Confirm the details on the next screen, then click Start Streaming.
Auto-subscribe other log groups to SumoCWLogsLambda function
If you want to collect logs from multiple Log Groups, you can use Sumo’s LogGroup Lambda Connector to subscribe additional Log Groups to the Lambda function. To do so, follow the instructions in Auto-Subscribe AWS Log Groups to a Lambda Function. When you edit the CloudFormation template for the connector, point the LAMBDA_ARN environment variable to the SumoCWLogsLambda function.
Alternate collection methods
If you can't use AWS Lambda or CloudFormation to collect logs from CloudWatch, choose one of the following methods:
A Lambda function without CloudFormation. To manually configure a Lambda function, see Collect Amazon CloudWatch Logs with Lambda Function.
:::note The Lambda function is not as comprehensive or robust as the CloudFormation template, because it does not include the alarm resources. :::
Amazon Kinesis. If AWS Lambda is not available to you, or you need increased delivery reliability, review how to add Amazon Kinesis to the integration as described in AWS Kinesis Firehose for Logs Source.
The Sumo Logic Collector and a Script. If you have a relatively small amount of CloudWatch logs to collect, and you do not want to set up any additional AWS infrastructure, you can install the Sumo Logic Collector agent locally, and run a script that we have developed for CloudWatch logs, with a special focus on Amazon VPC Flow Logs. See the instructions for collecting CloudWatch logs using a collector script.