MongoDB - OpenTelemetry Collector

MongoDB is a source-available cross-platform document-oriented database program. The Sumo Logic app for MongoDB supports logs and metrics from the open source version of MongoDB. The App is tested on the 4.4.4 version of MongoDB.
MongoDB logs are sent to Sumo Logic through OpenTelemetry filelog receiver.
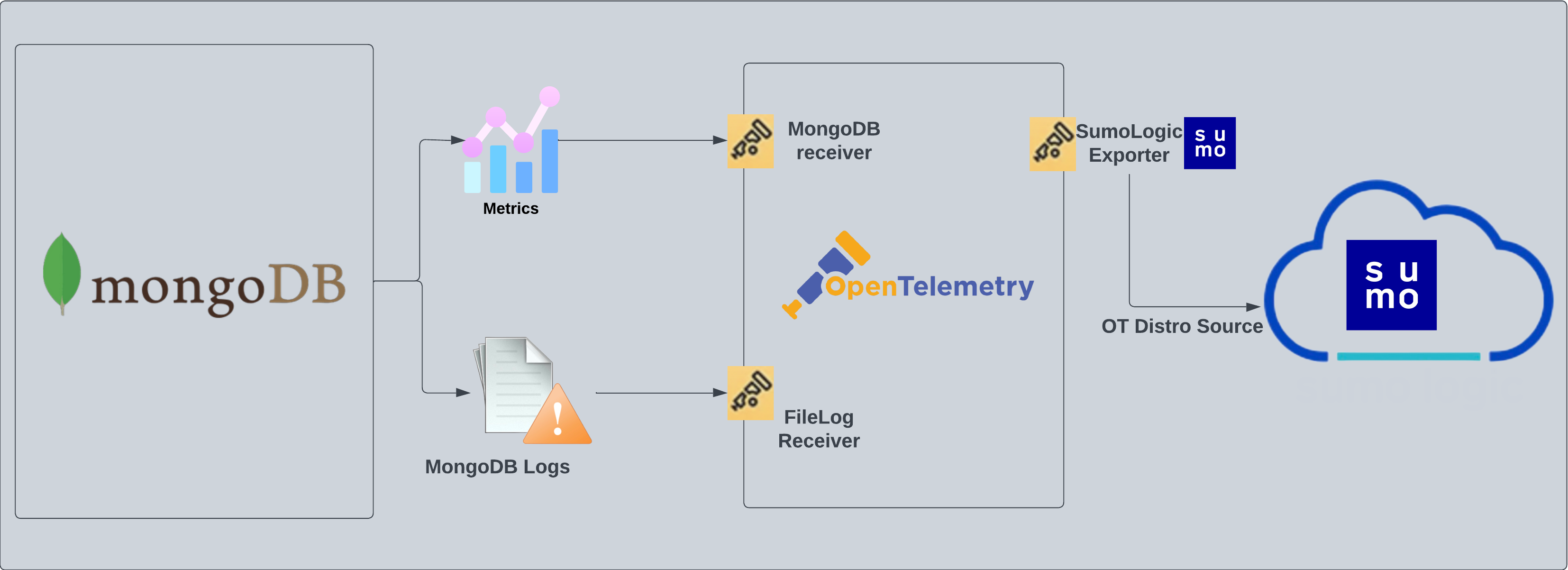
Log Types
The MongoDB logs are generated in files as configured in the configuration file /var/log/mongodb/mongodb.log. For more details on MongoDB logs, see this link.
Fields creation in Sumo Logic for MongoDB
Following are the Fields which will be created as part of MongoDB App install if not already present.
db.cluster.name. User configured. Enter a name to identify this MongoDb cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.db.system. Has fixed value of mongodb.deployment.environment. User configured. This is the deployment environment where the Mongodb cluster resides. For example: dev, prod or qa.sumo.datasource. has a fixed value of mongodb.
Prerequisites
By default, MongoDB logs are stored in a log file.
- Configure logging verbosity in MongoDB : MongoDB logs have six levels of verbosity. All logging settings are located in MongoDB.conf. To select a level, set loglevel to one of:
- 0 is the MongoDB's default log verbosity level, to include Informational messages.
- 1 to 5 increases the verbosity level to include Debug messages.
- Configure MongoDB to log to a Local file: Configuring MongoDB logs to go to log files. By default, MongoDB logs are stored in
/var/log/mongodb/mongodb.log. The default directory for log files is listed in the MongoDB.conf file. To configure the log output destination to a log file, use one of the following settings, either in the configuration file or command-line:- Configuration file: The systemLog.destination option for file.
Configure MongoDB Logs Collection
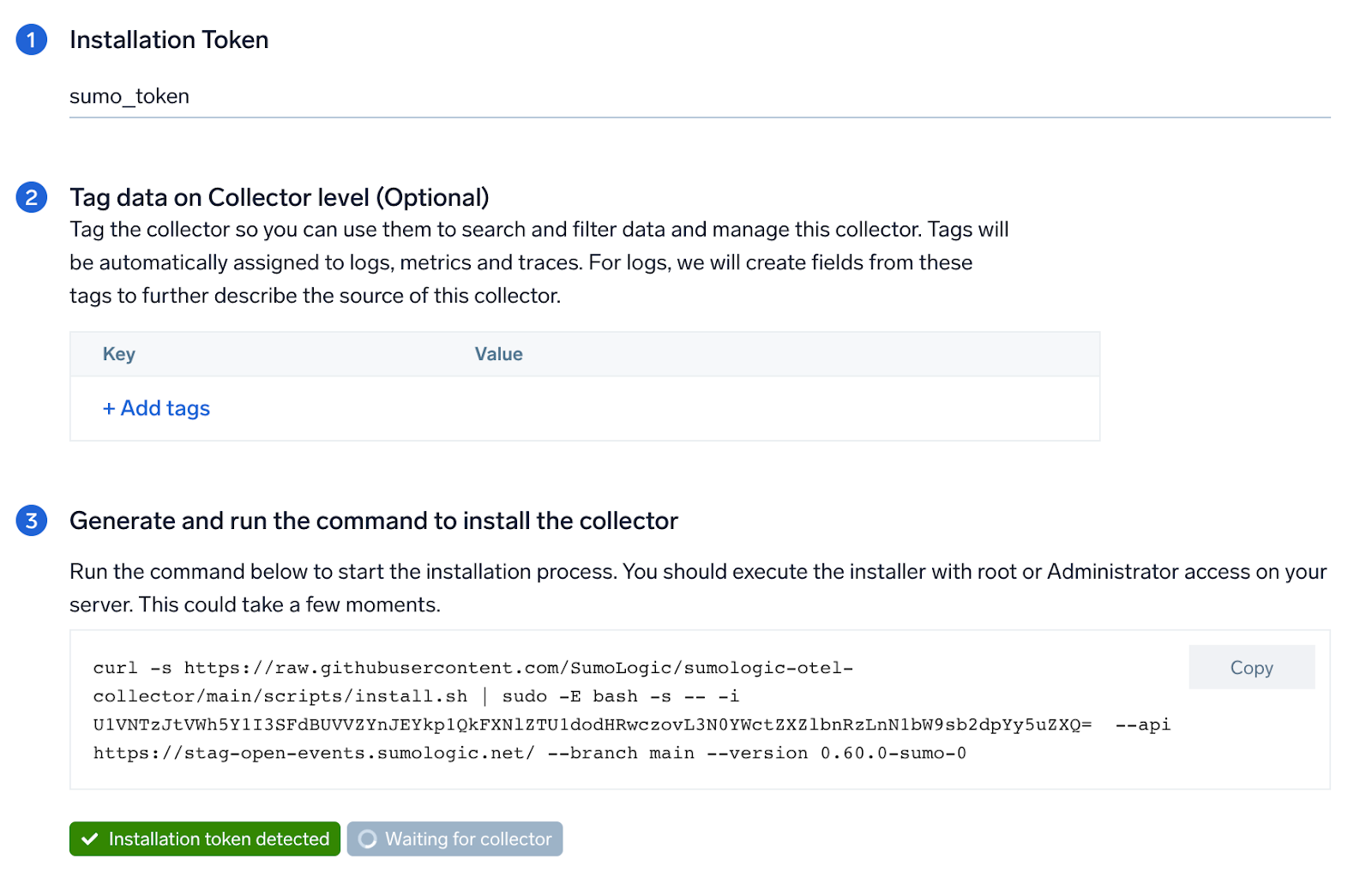
Step 1: Set up Collector
If you want to use an existing OpenTelemetry Collector, you can skip this step by selecting the Use an existing Collector option.
To create a new Collector:
- Select the Add a new Collector option.
- Select the platform where you want to install the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Collector.
This will generate a command that you can execute in the machine environment you need to monitor. Once executed, it will install the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Collector.
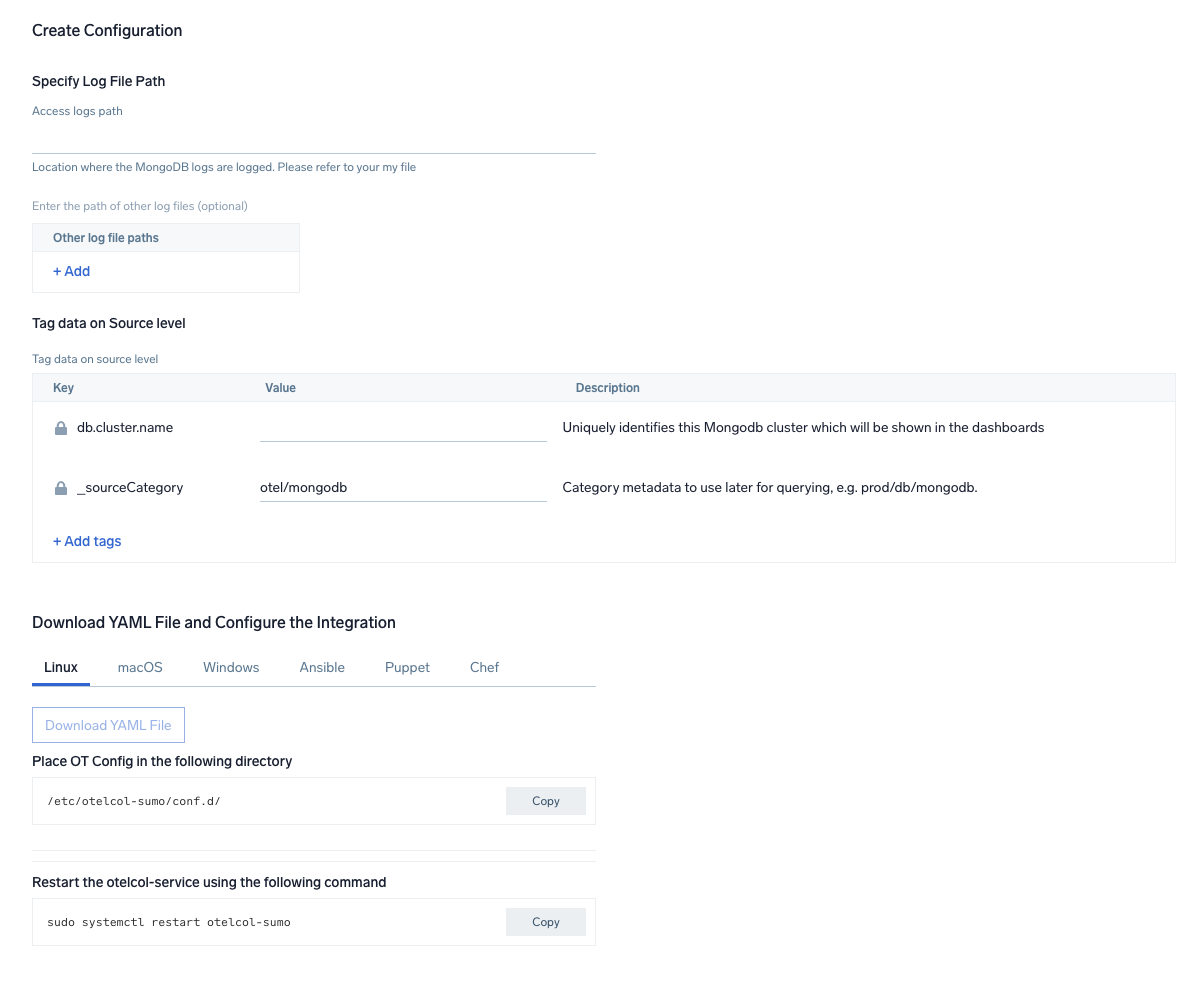
Step 2: Configure integration
In this step the user needs to provide the path to the mongo db log file configured as part of above steps. Typically the logs are located at the location: /var/log/mongodb/mongodb.log.
You can add any custom fields which you want to tag along with the data ingested in Sumo. Click on the Download YAML File button to get the yaml file.
Step 3: Send logs to Sumo
Once you have downloaded the yaml file as described in the previous step, follow the below steps based on your platform.
- Linux
- Windows
- macOS
- Copy the yaml file to
/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/folder in the Mongodb instance which needs to be monitored. - restart the collector using:
sudo systemctl restart otelcol-sumo
- Copy the yaml file to
C:\ProgramData\Sumo Logic\OpenTelemetry Collector\config\conf.dfolder in the machine which needs to be monitored. - Restart the collector using:
Restart-Service -Name OtelcolSumo
- Copy the yaml file to
/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/folder in the Mongodb instance which needs to be monitored. - Restart the otelcol-sumo process using:
otelcol-sumo --config /etc/otelcol-sumo/sumologic.yaml --config "glob:/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/*.yaml"
After successfully executing the above command, Sumo Logic will start receiving data from your host machine.
Click Next. This will install the app (dashboards and monitors) to your Sumo Logic Org.
Dashboard panels will start to fill automatically. It's important to note that each panel fills with data matching the time range query and received since the panel was created. Results won't immediately be available, but within 20 minutes, you'll see full graphs and maps.
Sample Log Message
{
"t":{
"$date":"2021-05-21T10:22:57.373+00:00"
},
"s":"I",
"c":"NETWORK",
"id":51800,
"ctx":"conn500659",
"msg":"client metadata",
"attr":{
"remote":"127.0.0.1:49472",
"client":"conn500659",
"doc":{
"application":{
"name":"MongoDB Shell"
},
"driver":{
"name":"MongoDB Internal Client",
"version":"4.4.4"
},
"os":{
"type":"Linux",
"name":"PRETTY_NAME=\"Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster)\"",
"architecture":"x86_64",
"version":"Kernel 4.4.0-62-generic"
}
}
}
}
Sample Query
Dashboard: MongoDB - Errors and Warnings, Panel: Errors by Component
deployment.environment=* db.cluster.name=* sumo.datasource=mongodb | json "log" as _rawlog nodrop
| if (isEmpty(_rawlog), _raw, _rawlog) as _raw
| json field=_raw "t.$date" as timestamp
| json field=_raw "s" as severity
| json field=_raw "c" as component
| json field=_raw "ctx" as context
| json field=_raw "msg" as msg
| where severity in ("E")
| count by component
Viewing MongoDB Dashboards
If no relevant data was received within the time range of the Panel, the Panel will be empty.
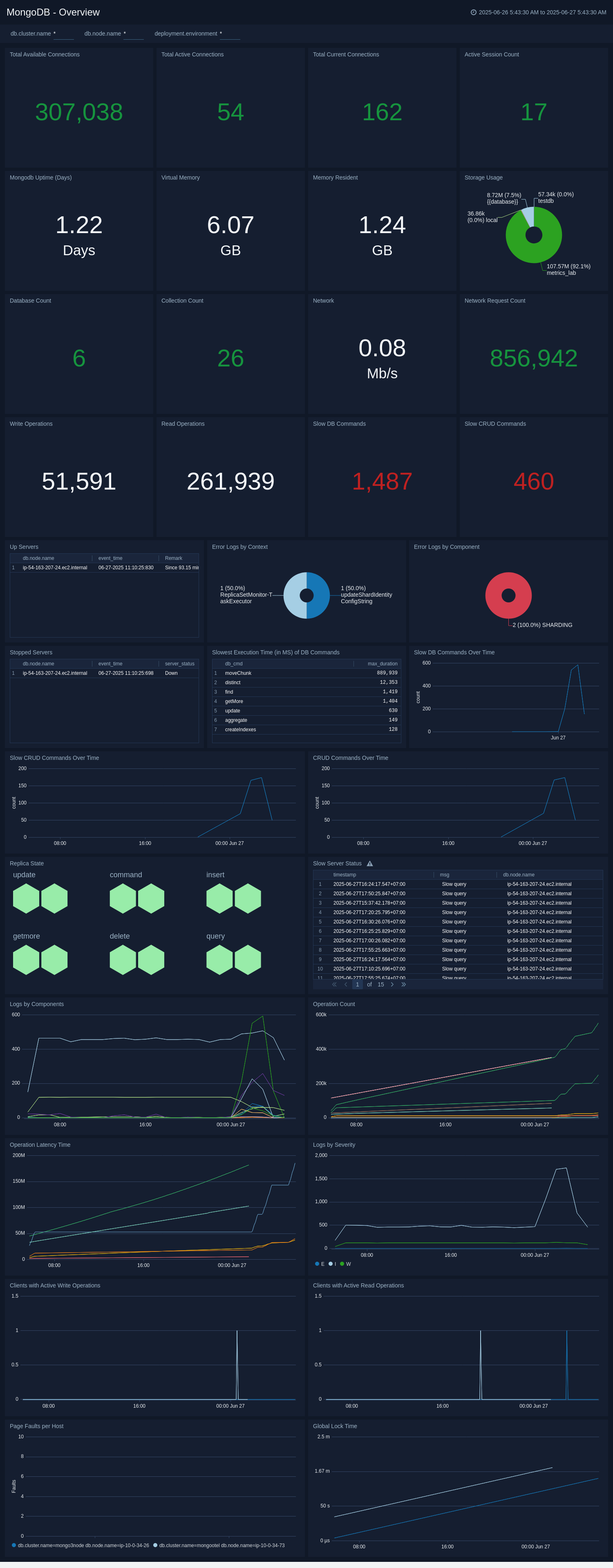
Overview
The MongoDB - Overview dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of MongoDB health, performance and problems causing errors.
Use this dashboard to:
- Identify Slow CRUD and DB commands.
- Gain insights into Errors logs by component and context.
- Number of up servers.
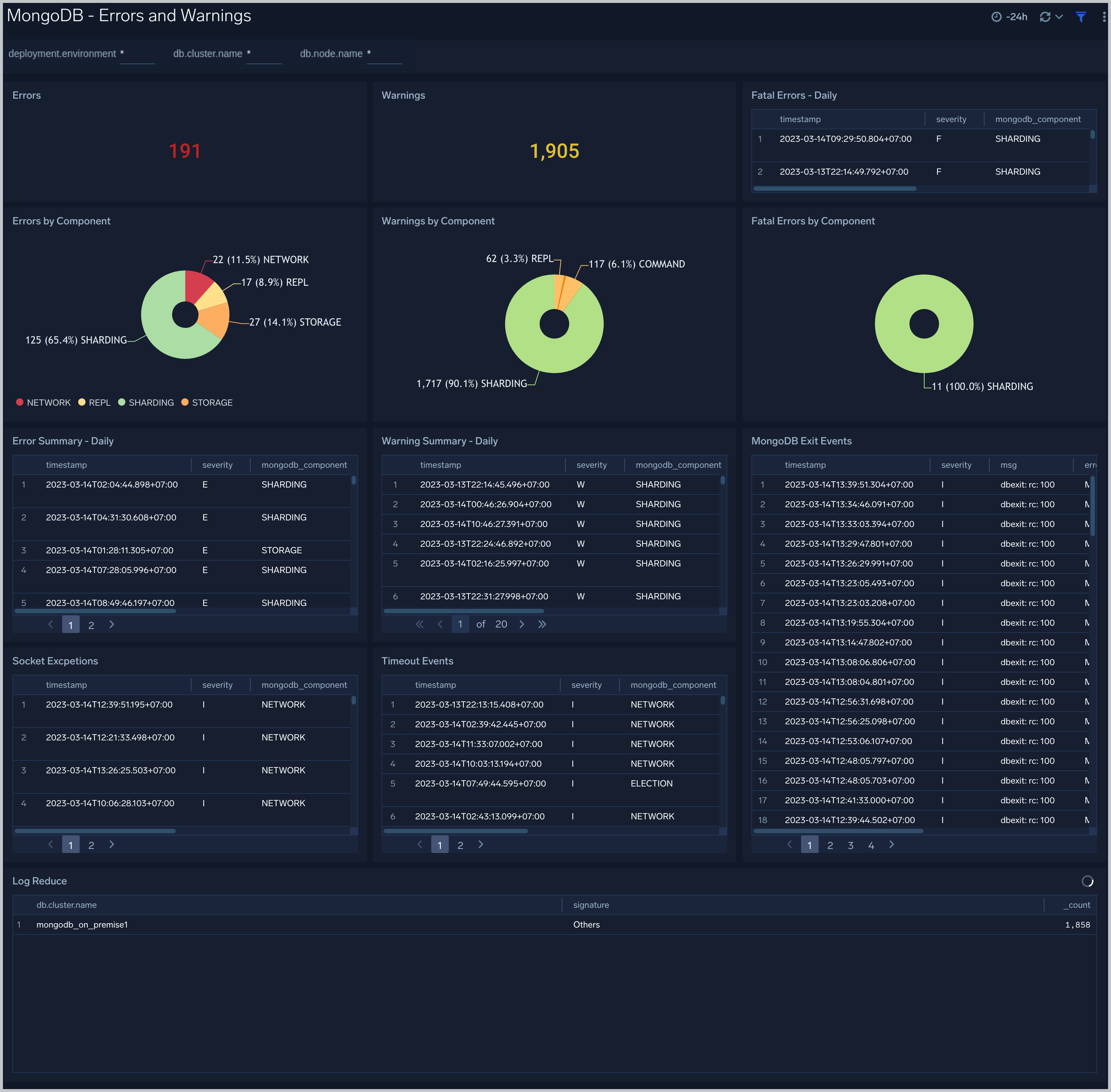
Errors and Warnings
The MongoDB - Errors and Warnings dashboard shows errors and warnings by the MongoDB component.
Use this dashboard to:
- Determine components producing multiple errors or warnings.
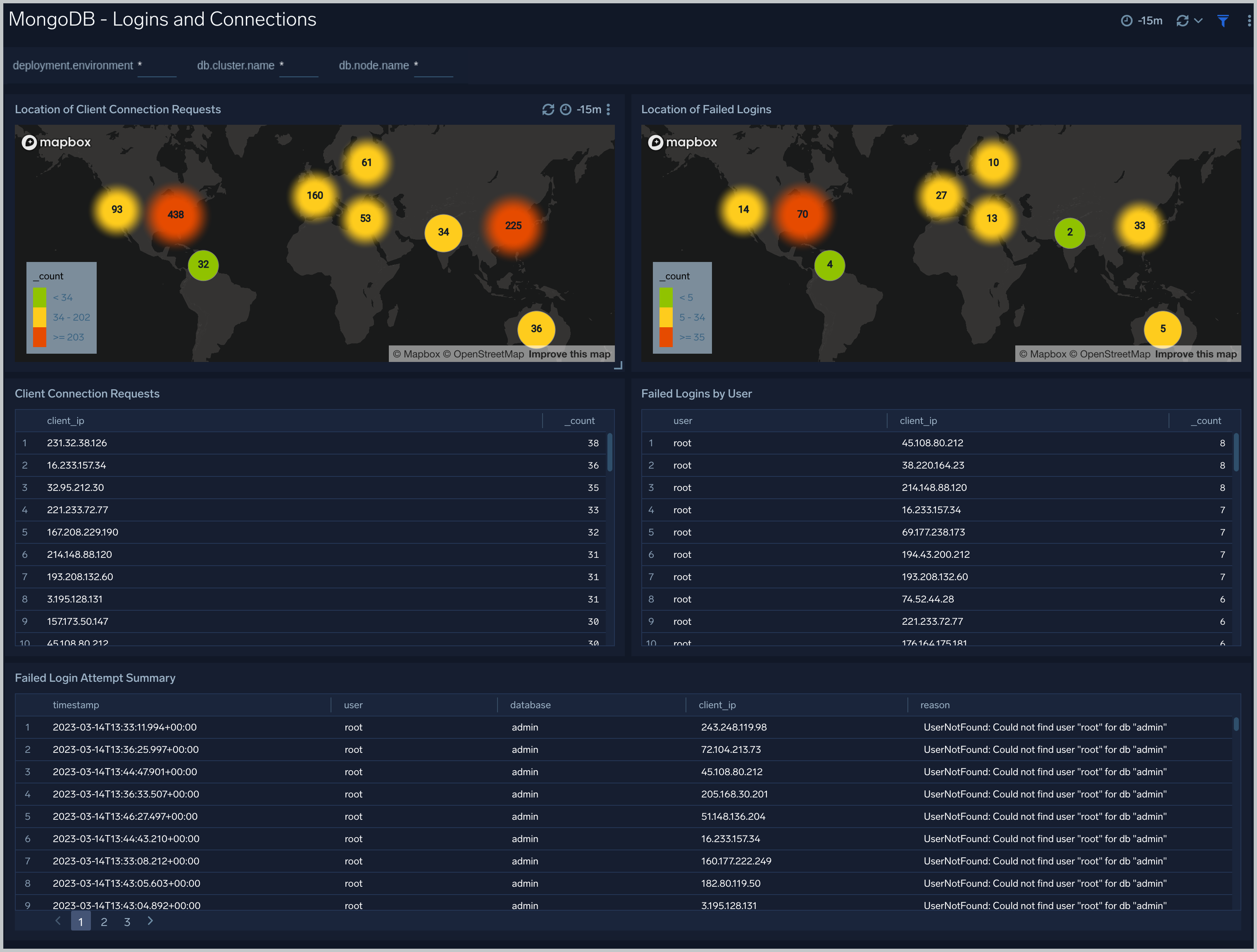
Logins and Connections
The MongoDB - Logins and Connections dashboard shows geo location of client connection requests, failed connection logins by geo location, and count of failed login attempts.
Use this dashboard to:
- Determine potential hacking attempts.
- Determine location of attacks.
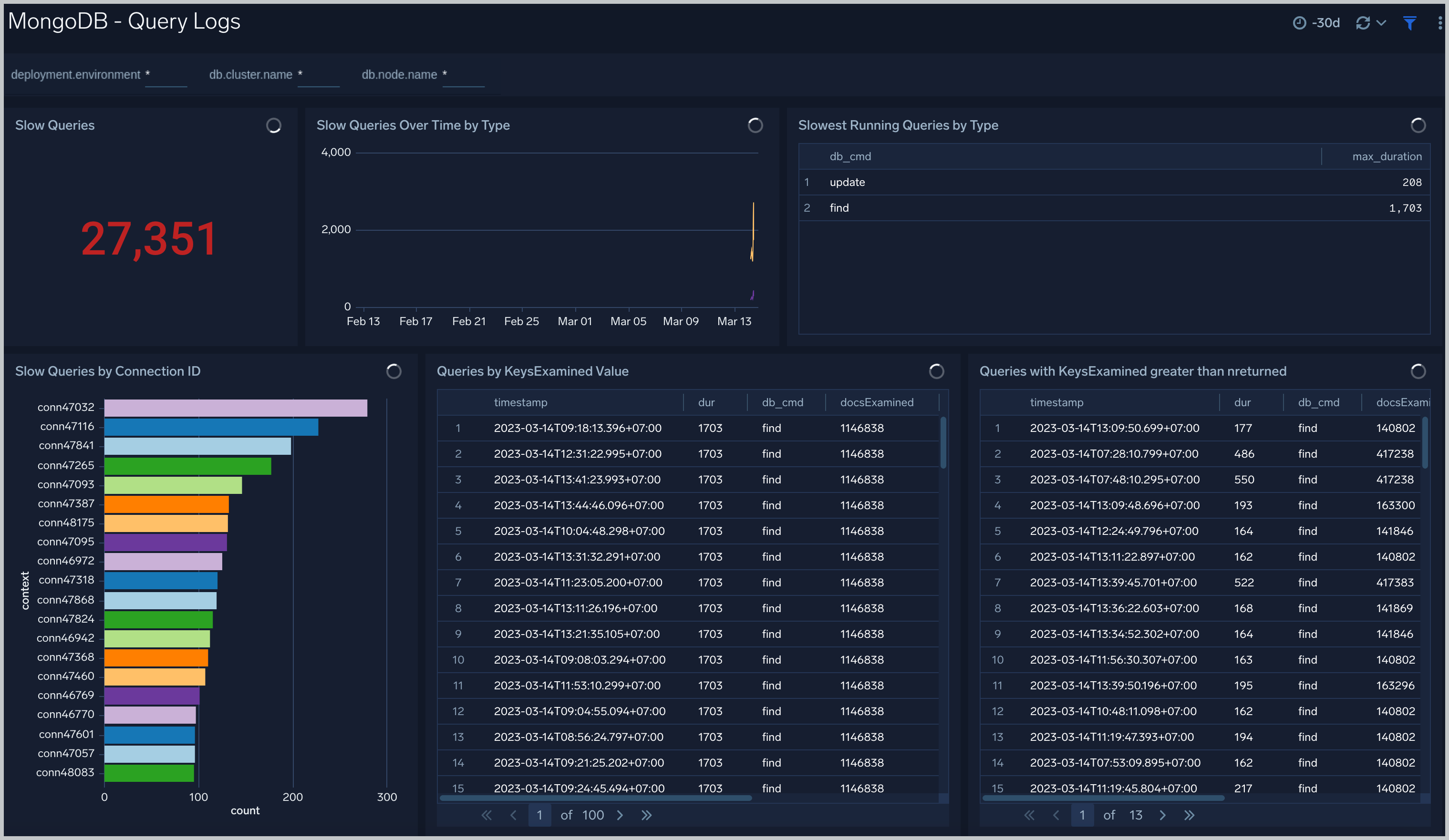
Query Logs
The MongoDB - Query Logs dashboard shows read and write query trends.
Use this dashboard to:
- Monitor abnormal spikes in Query volume.
- Identify the read versus write ratio of your application queries. Adjusting indexes to improve query performance.
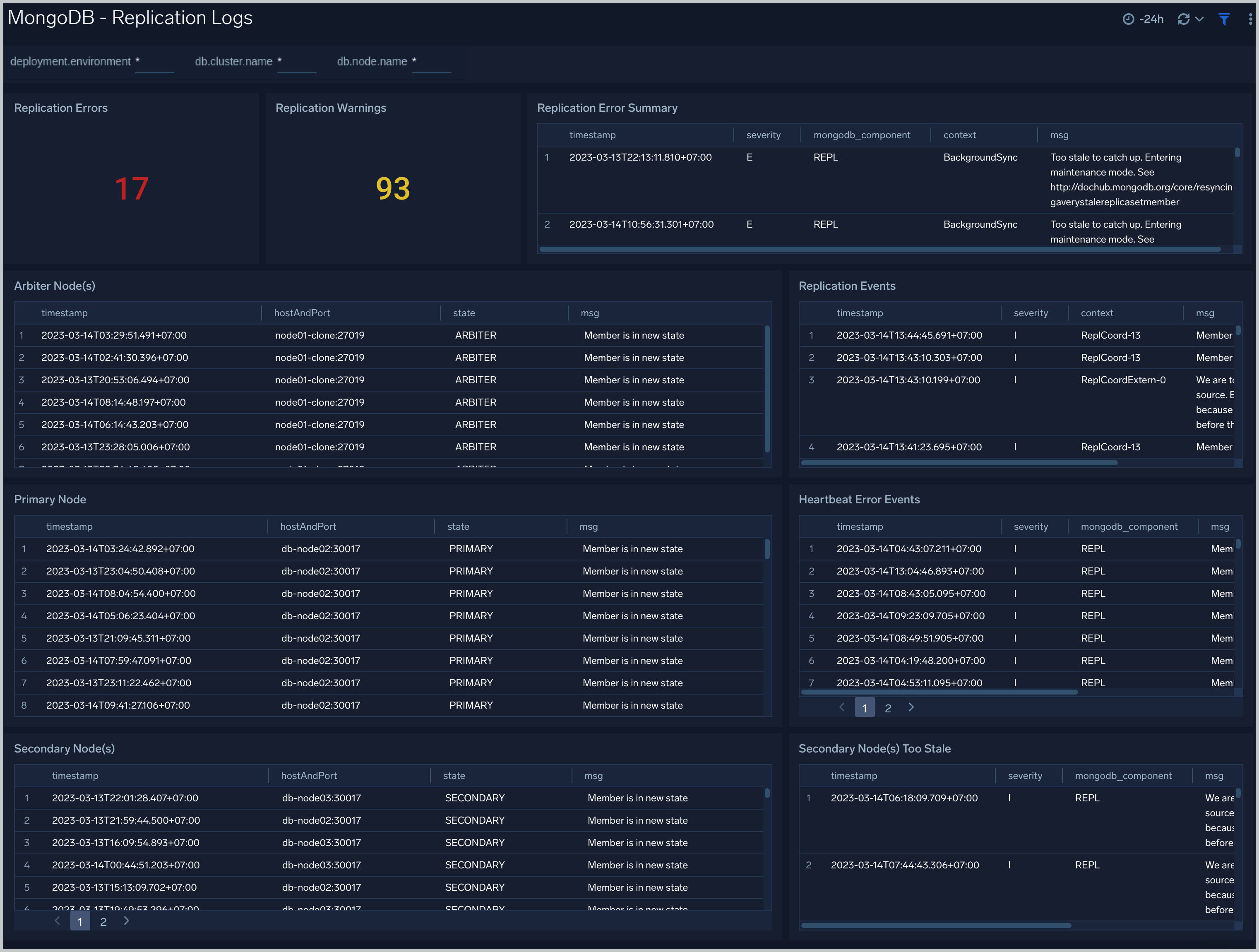
Replication Logs
The MongoDB - Replication Logs dashboard shows replica deletes/updates/inserts trend and replica state.
Use this dashboard to:
- Monitor replication state and replication events like inserts/updates/commands per second.
- Track Replication Oplog window to identify replication delay
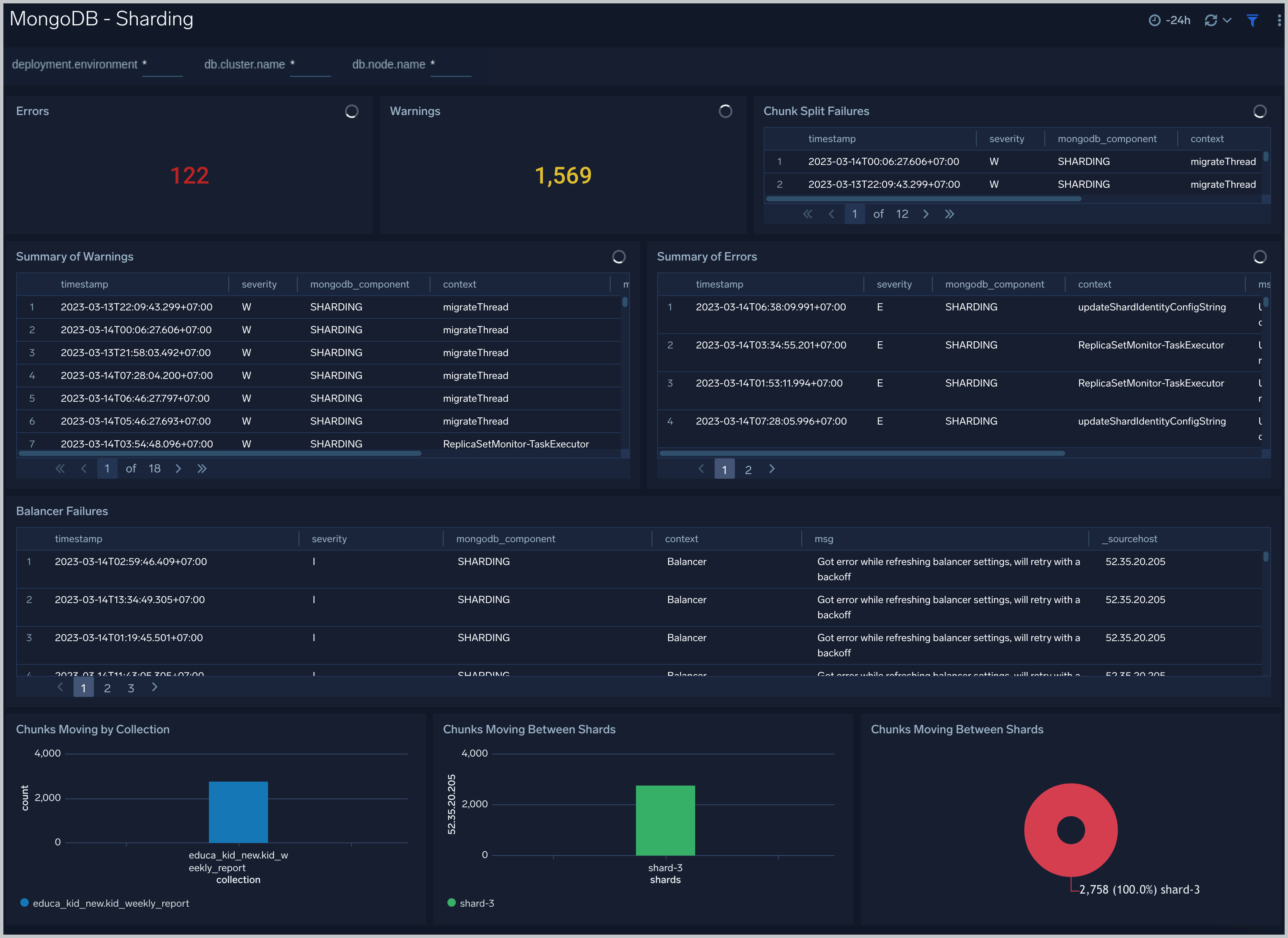
Sharding
The MongoDB - Sharding dashboard dashboard shows sharding related errors, events, failures and number of chunks moving between shards.
Use this dashboard to:
- Identify Sharding errors and warnings.
- Gain insights into Chunk operations.